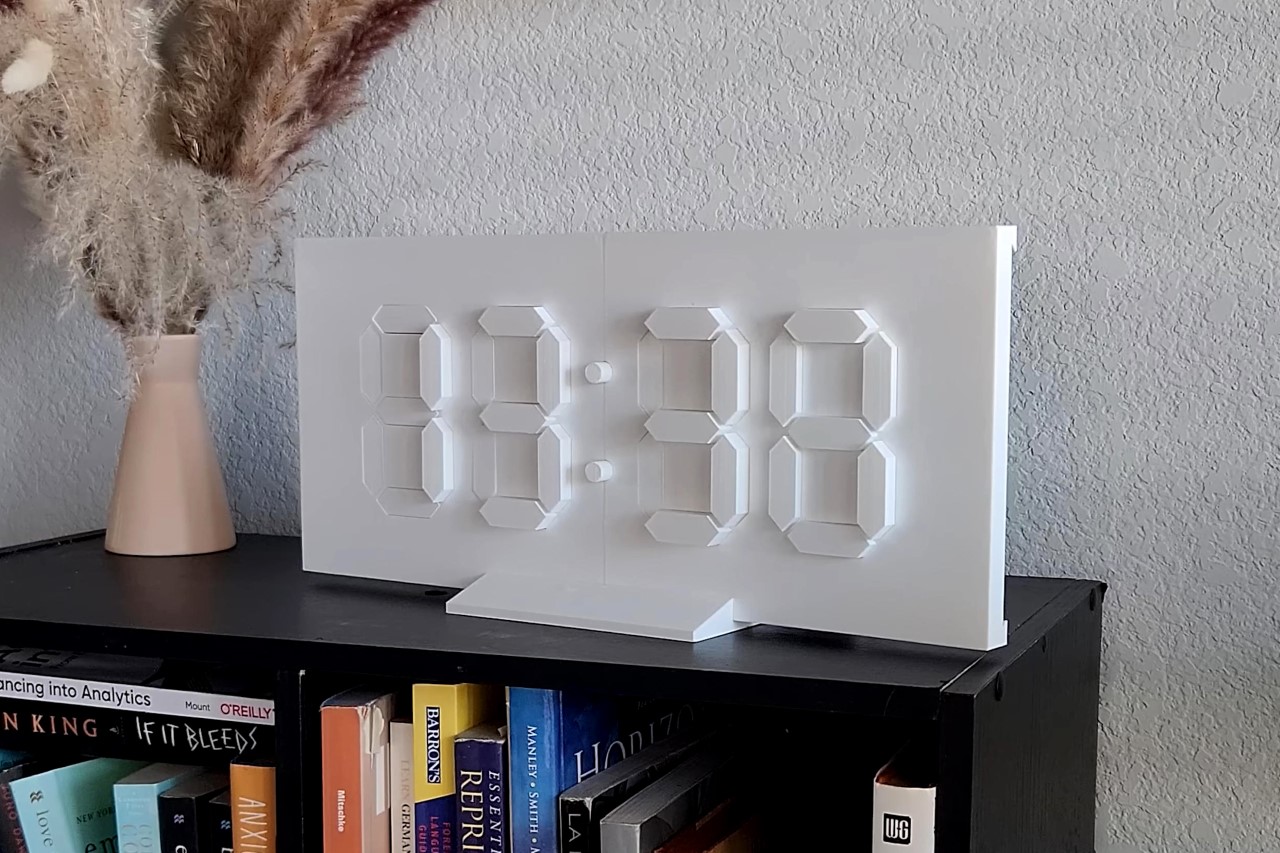
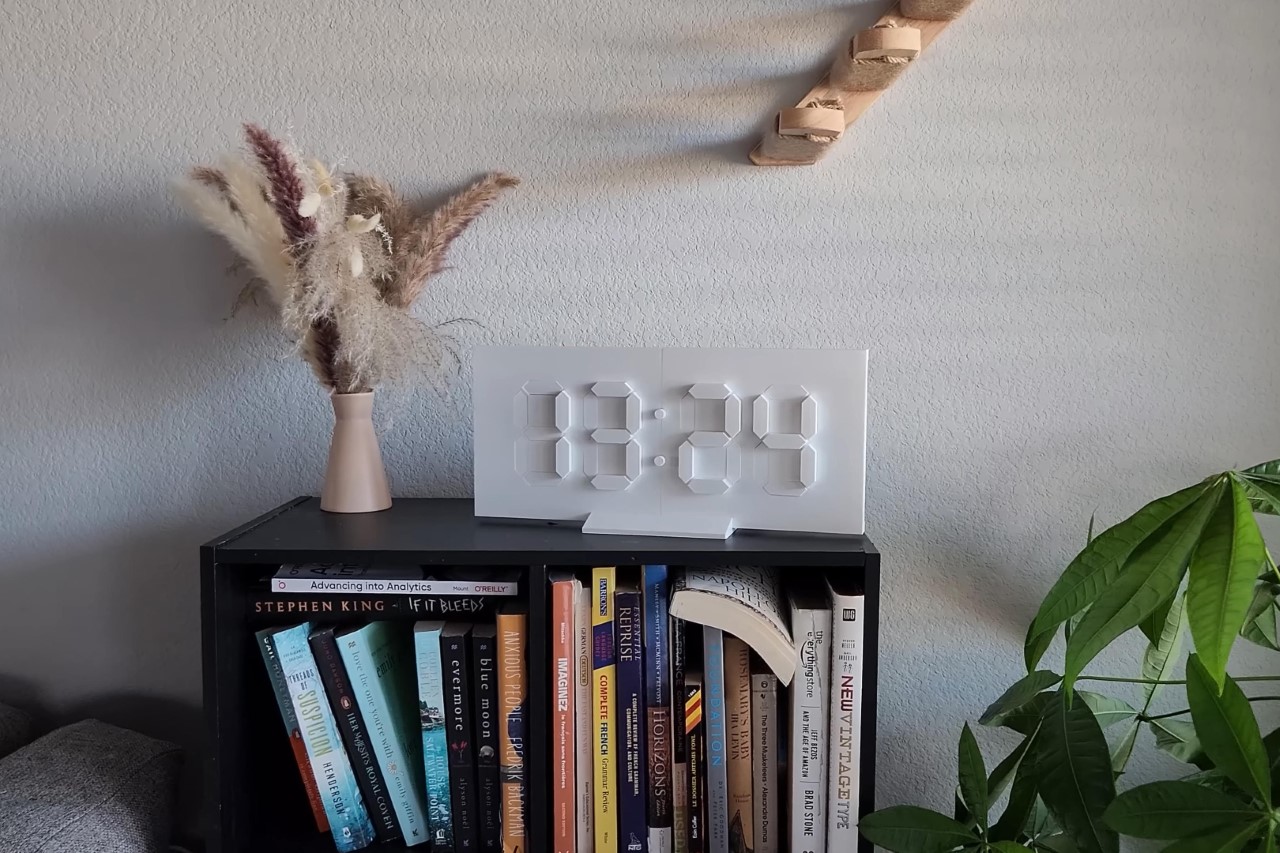
Let’s face it, that thumbnail probably brought you here. Outwardly, the Minimal Kinetic Clock is just a flat piece of white plastic, but thanks to a few moving parts, it assumes a three-dimensional shape that tells the time. Strategically place it in an area with dramatic lighting and the time stands out through how the clock captures highlights and casts shadows.
The project comes courtesy YouTuber Lukas Deem, who meticulously builds the clock from scratch using bespoke 3D-printed parts, an Arduino Mega SoC, and a handful of motors and sensors (while graciously documenting the process for all of us to see. Lukas walks the viewers through the whole procedure, which took multiple iterations and fixes to put together, even detailing out a special stand he made for the clock once it was up and running. The final result looks gorgeous, and I can only imagine how wonderful it would look if Lukas mounted a stretchy white cloth on the front, allowing the parts to push through to create the shape of every number. If you’re reading this, Lukas… give it a shot!
Designer: Lukas Deem (originally made by Jacky Mok)
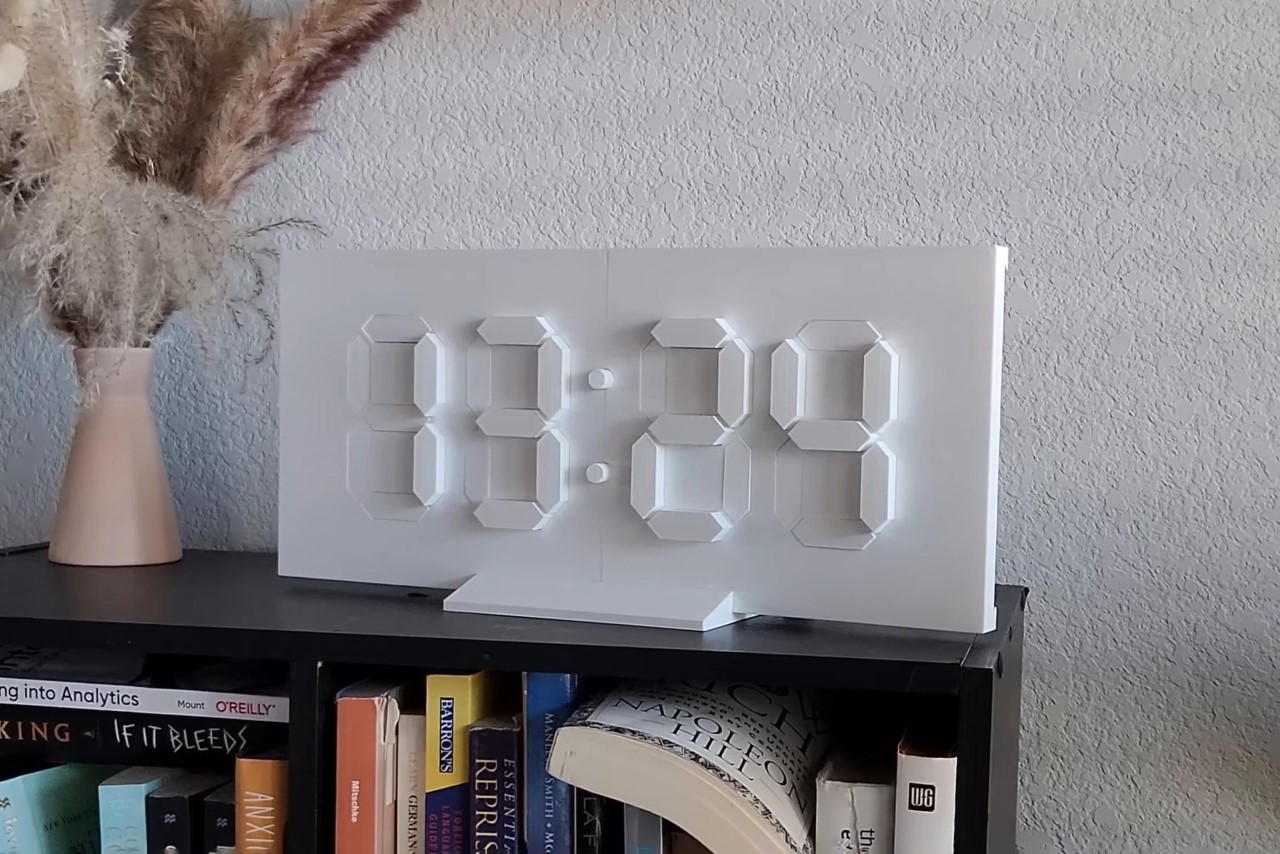

Lukas embarked on this venture with a clear goal: to build a clean, minimalistic kinetic clock that elevates the concept of timekeeping into kinetic art. The choice of materials was crucial to this endeavor. The project required two power supplies to ensure all components received adequate energy, white Hatchbox filament for its optimal quality for 3D printing, an off-brand Arduino Mega (from Elegoo), a sensor shield for the electronics, and 30 budget-friendly servos to bring the kinetic aspect to life. A real-time clock (RTC) module was also essential for maintaining accurate time.


The 3D printing process alone was a marathon, consuming approximately 85 hours, excluding the time spent on test prints and correcting mistakes. This phase underscored the meticulous attention to detail and patience required for such an intricate project.

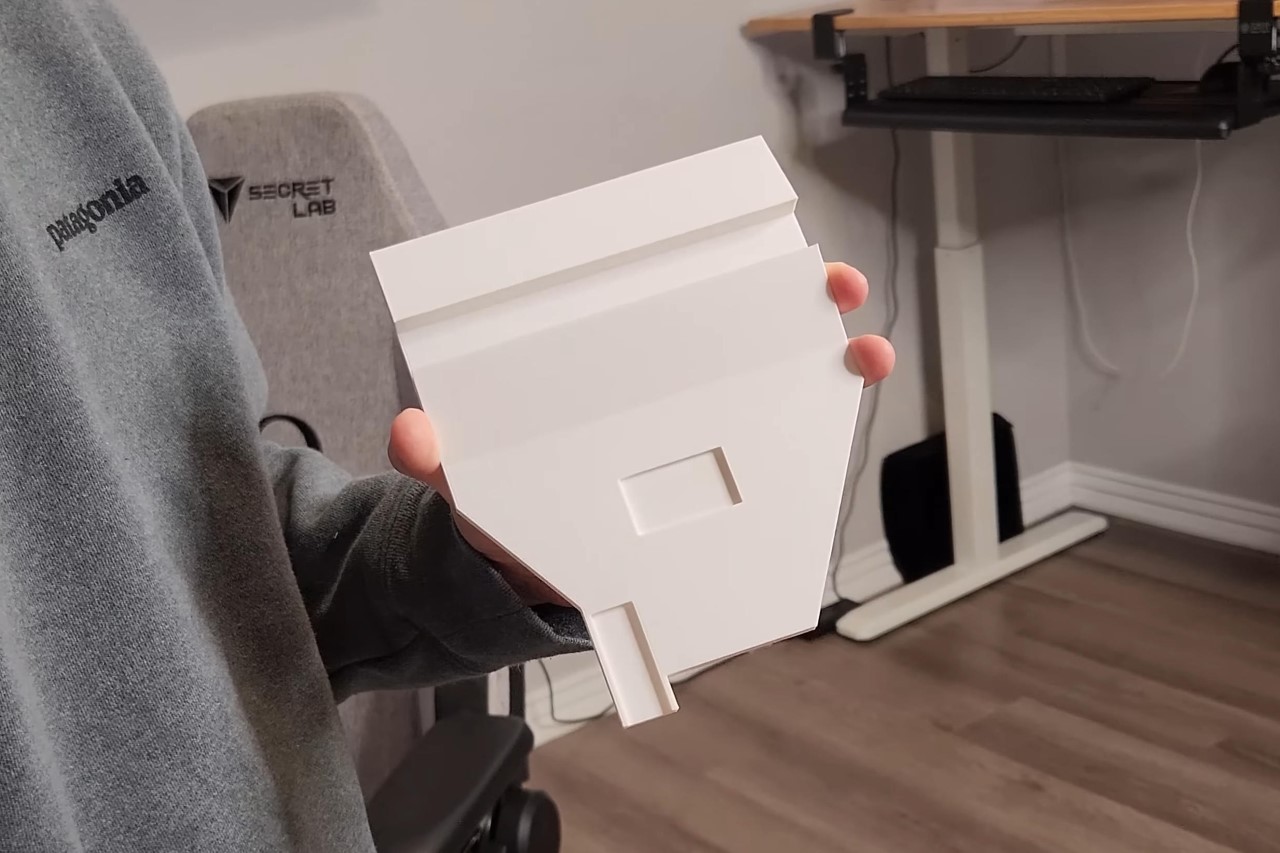
However, the assembly phase presented its own set of challenges. Each of the 30 servos underwent rigorous testing for functionality, with a critical step involving the calibration of these components to ensure the clock’s precise movement. One significant hurdle was the project’s power supply system. The challenge of efficiently powering both the Arduino and the sensor shield without resorting to an unwieldy setup led to a compromise: using two power plugs, a solution that, while not ideal, was necessary under the constraints of time and resources.


Design refinements were also an integral part of the process. The creator focused on cable management, using zip ties to maintain a neat appearance, and developed a new base design to enhance the clock’s stability and aesthetic appeal. These improvements aimed at making the clock not just a functional piece but also a polished work of art worthy of display.
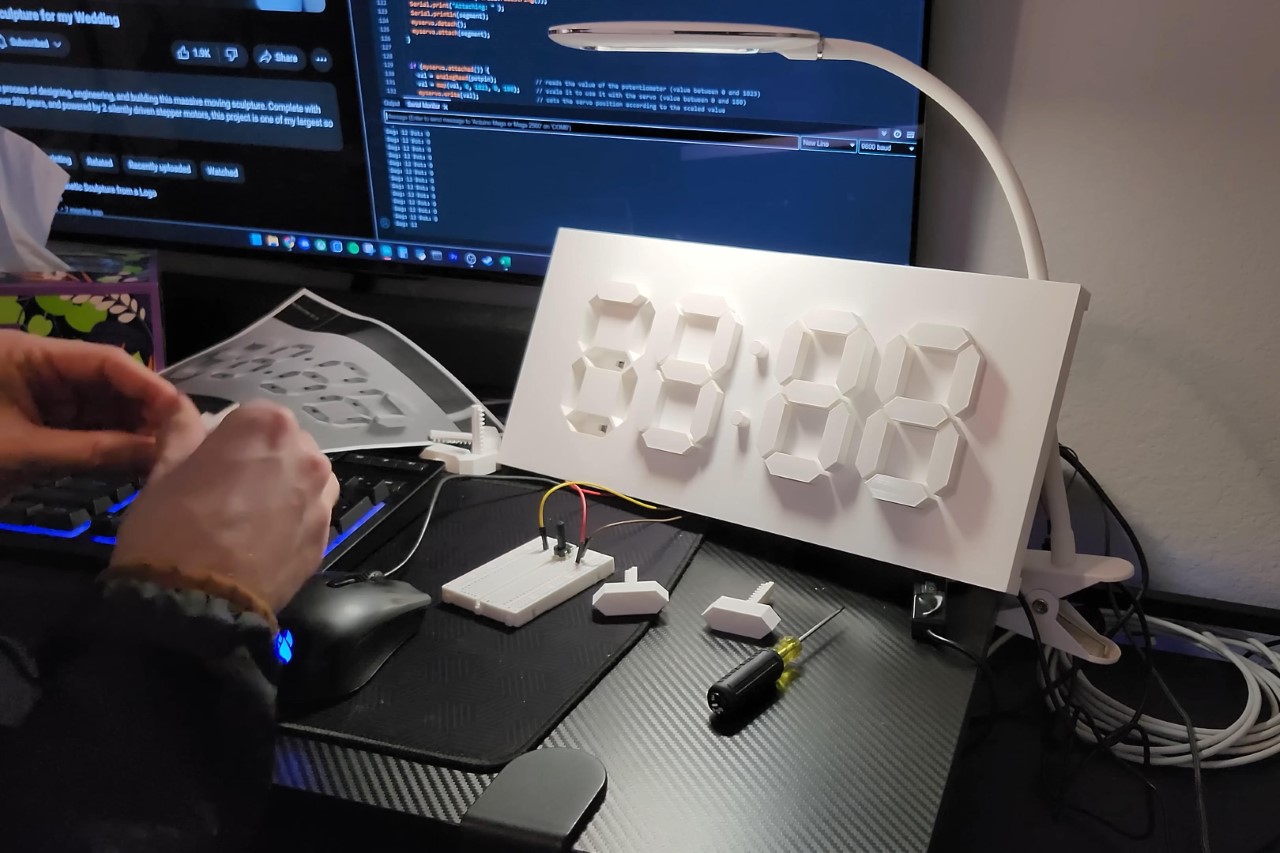

That being said, there was definitely room for improvement. Lukas pointed out that the servo motors in the clock weren’t particularly quiet, which meant this clock was a LOT noisier than your traditional ticking clock. However, it would do rather well in an open space like a living room, as opposed to being by your bedside or study table. Assembling the clock using hot glue also seemed to be a rather poor idea, given how it prevents you from disassembling/repairing/upgrading your clock after it’s built.

Lukas, however, isn’t the original creator of the clock. He credits the original design to Jacky Mok, who goes by the username ‘alstroemeria’ on Instructables. You can check out Jacky’s fully detailed build page on the Instructables website if you want to build your own Minimalist Kinetic Clock.







