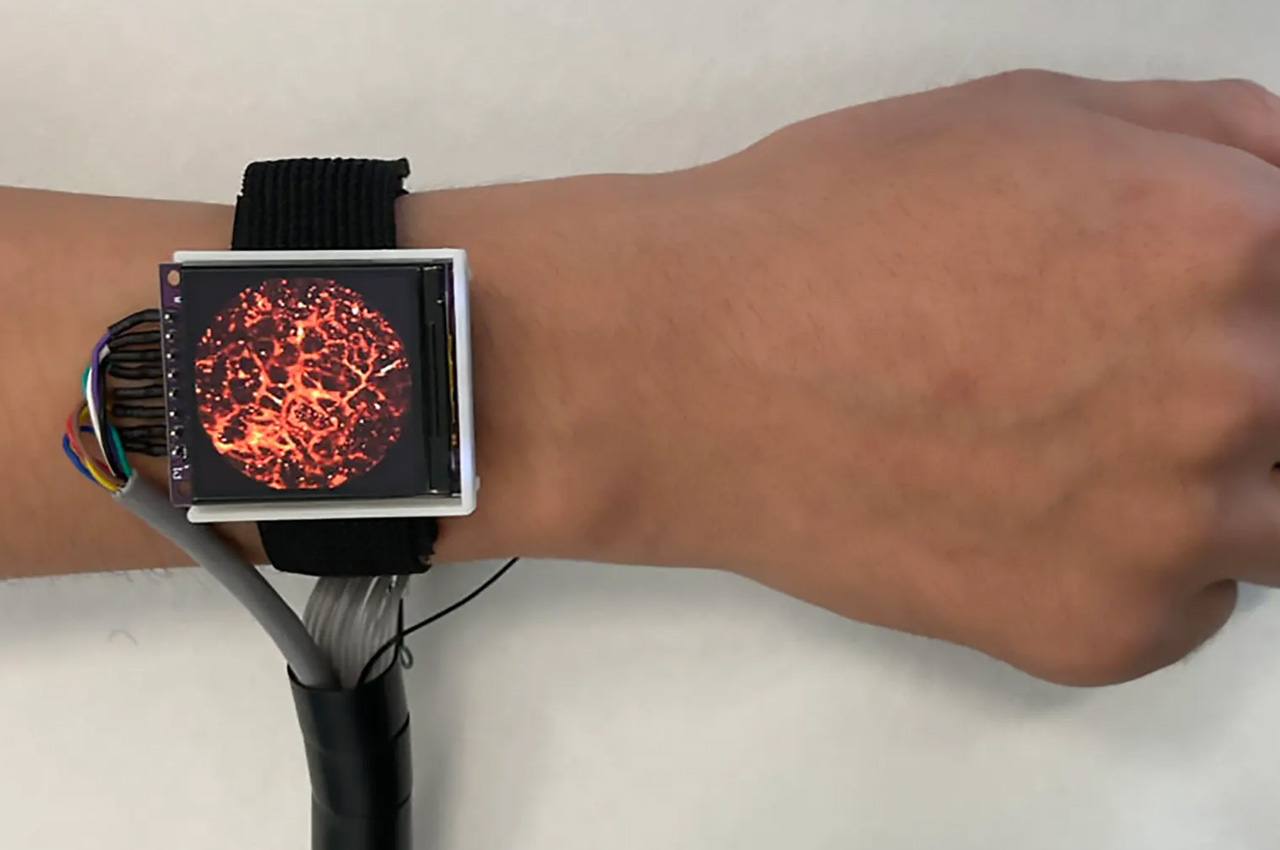
In a new and essential medical advancement, a team of researchers at the Southern University of Science and Technology in China has devised a wearable watch that can non-invasively monitor a wearer’s blood pressure, heart rate, and blood oxygen saturation by clicking photos of the blood vessels in the skin. For this, the high-tech watch uses photoacoustic imaging and checks the user’s heart health in real time without much hassle.
Photoacoustic imaging machines generally use light and sound waves to see and hear inside the body and capture high-resolution imagery of blood vessels to estimate oxygen saturation, skin conditions, and even cancer. Presently, these machines are bulky and require the user to visit the hospital. With the help of the Photoacoustic Imaging Watch, Chinese researchers have been able to miniaturize the tech to monitor how the wearer’s heart is working in real time, anywhere.
Designer: Southern University of Science and Technology
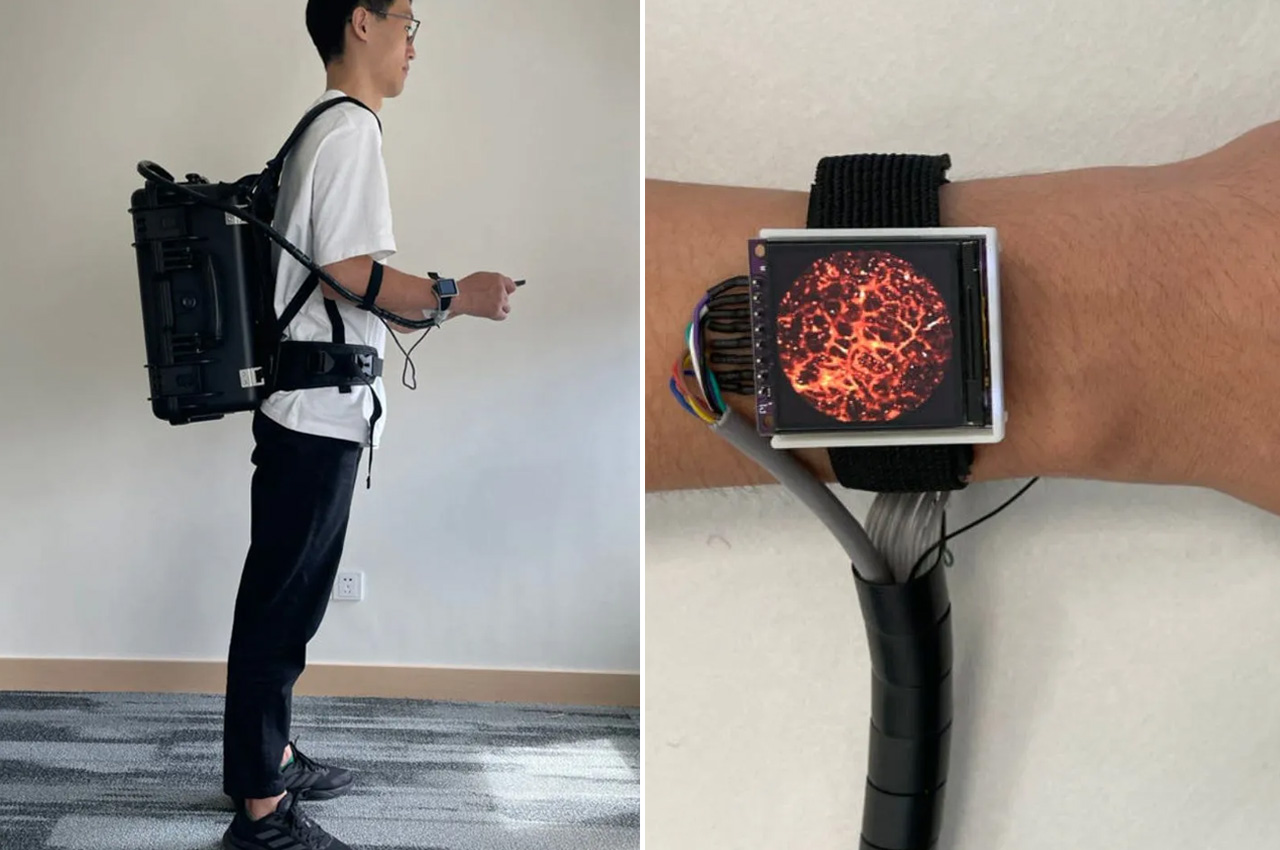
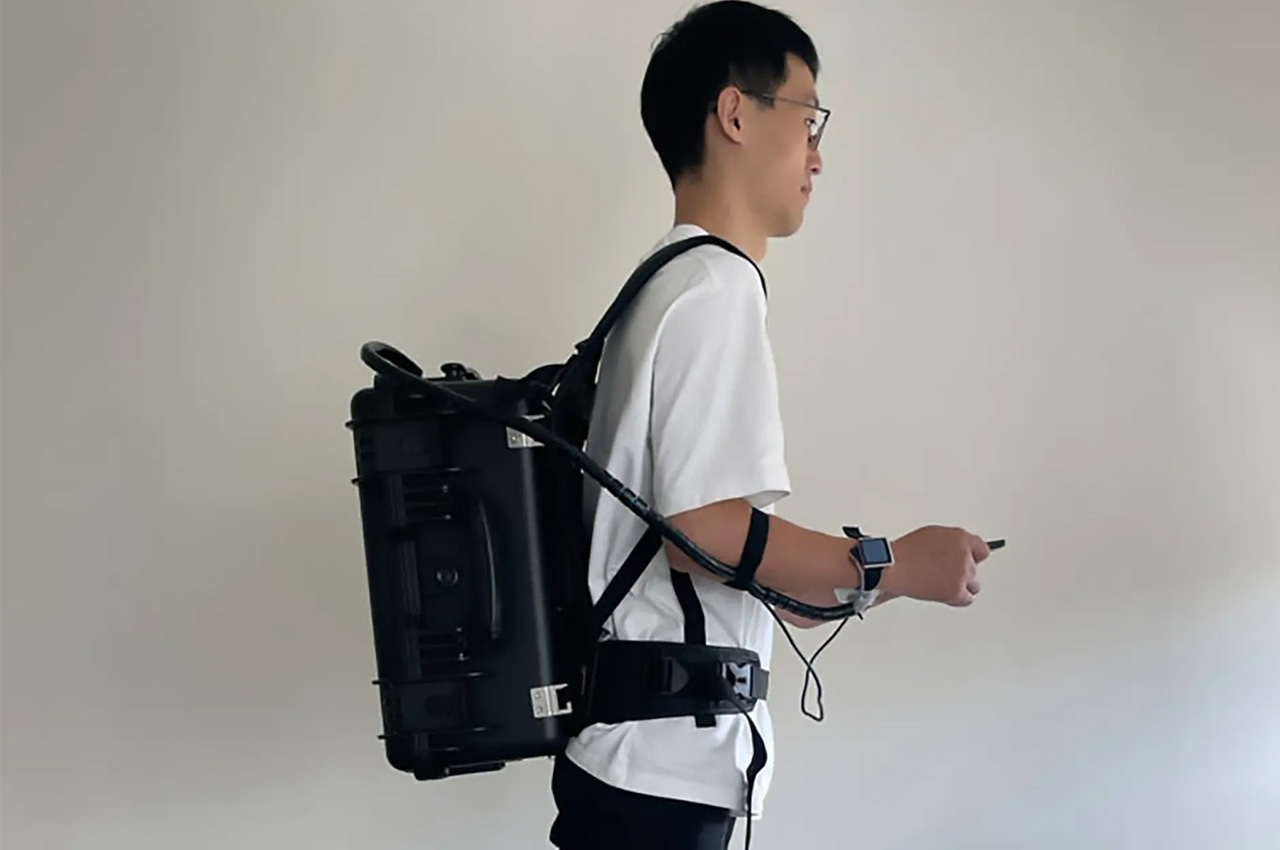
The watch, developed by SUST captures images of the blood vessels using tiny laser beams in the skin in high resolution. The watch is the imaging device and it is attached to a backpack that houses the entire hardware. With the watch on the wrist and backpack on the shoulder, the user should be able to check blood pressure, heart rate, and blood oxygen levels even while moving around freely.
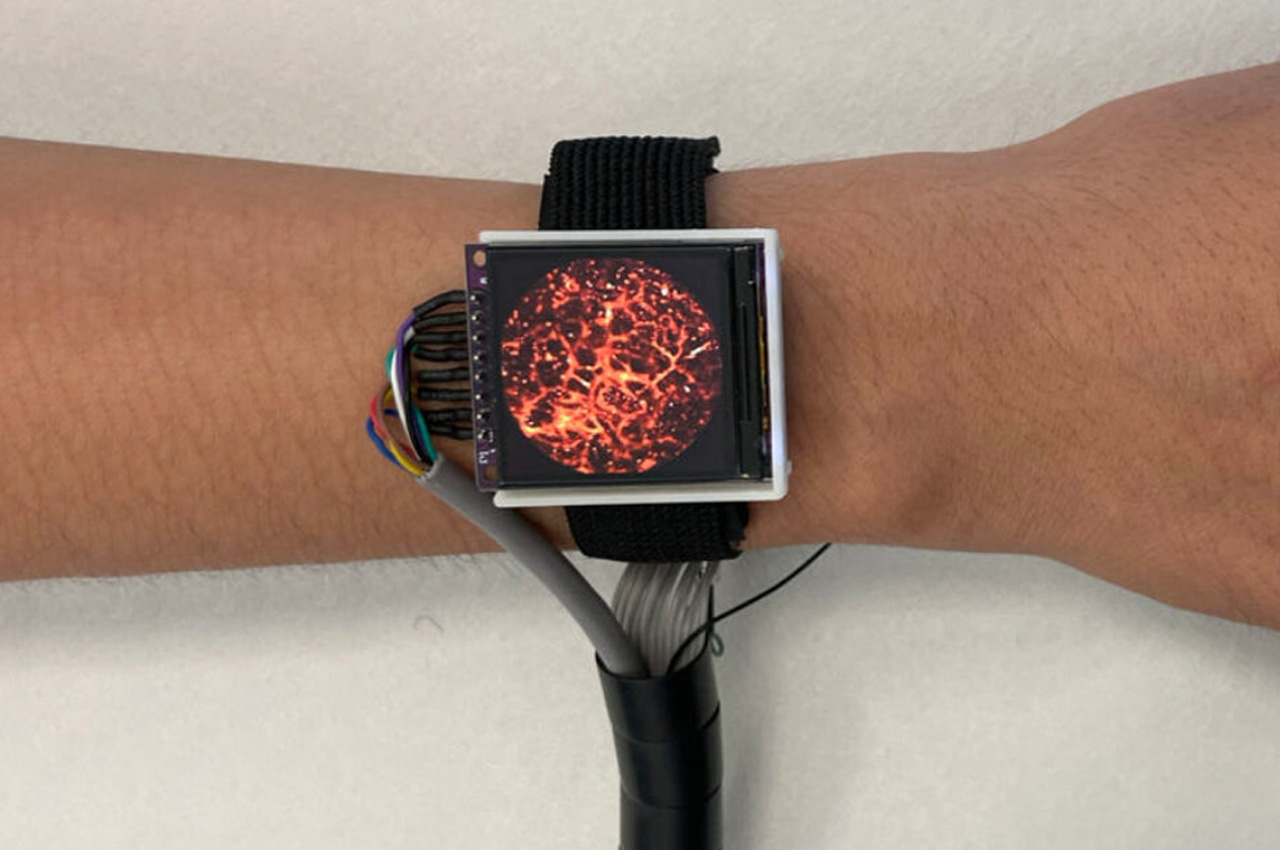
The backpack containing the hardware – laser and power supply – weighs about seven kilograms. The lightweight backpack can be carried around with ease while it allows the laser to focus and capture images of the tiniest of blood vessels in the skin around a 3 mm field of view. The new imaging system is currently in testing under various conditions, and it has been seen as a successful, convenient, and mobile alternative.

This “miniaturized wearable imaging system” can be used in “community health centers for preliminary disease diagnosis” or for “long-term monitoring of parameters related to blood circulation.” Also, the system can be handy in “early detection of skin diseases.” The researchers are trying to make an even smaller laser beam to make the wearable photoacoustic imaging system more portable, maybe even small enough to eliminate the backpack from the design.