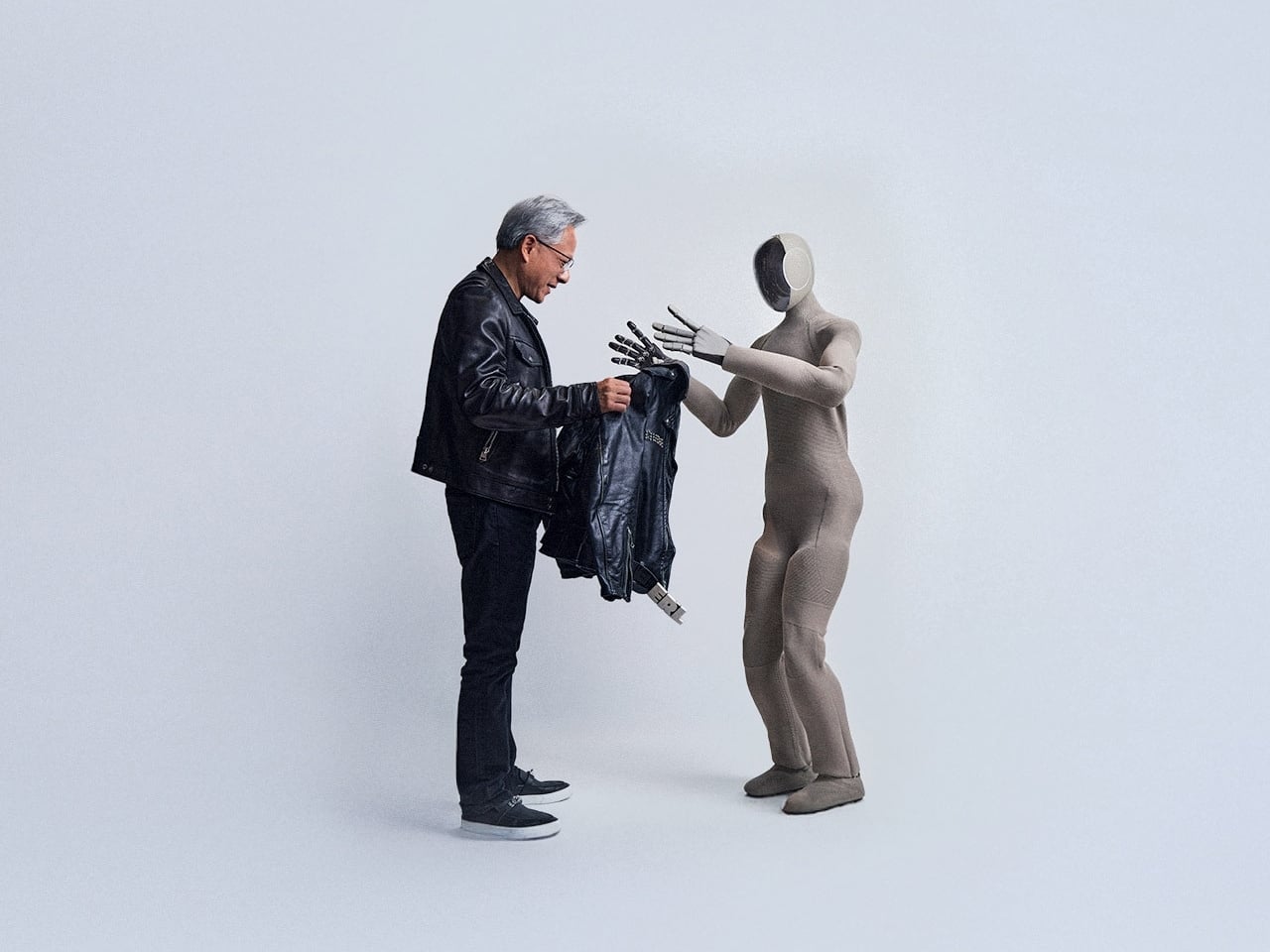
Step into a reality where science fiction blends effortlessly with everyday life. Human-like robots, or humanoids, are no longer distant fantasies as they are being designed to fit naturally into our routines. While their presence can feel intimidating at first, understanding their purpose shows a path toward enhanced comfort, support, and convenience. Like a thoughtfully designed home anticipating your every need, these robots are meant to enrich daily living rather than disrupt it.
Beyond novelty, these intelligent machines offer practical solutions for modern challenges. By mirroring human interaction and form, they become approachable helpers, assisting in homes, hospitals, and communities with tasks that require precision, care, and a human touch.
1. Bridging the Empathy Gap in Care
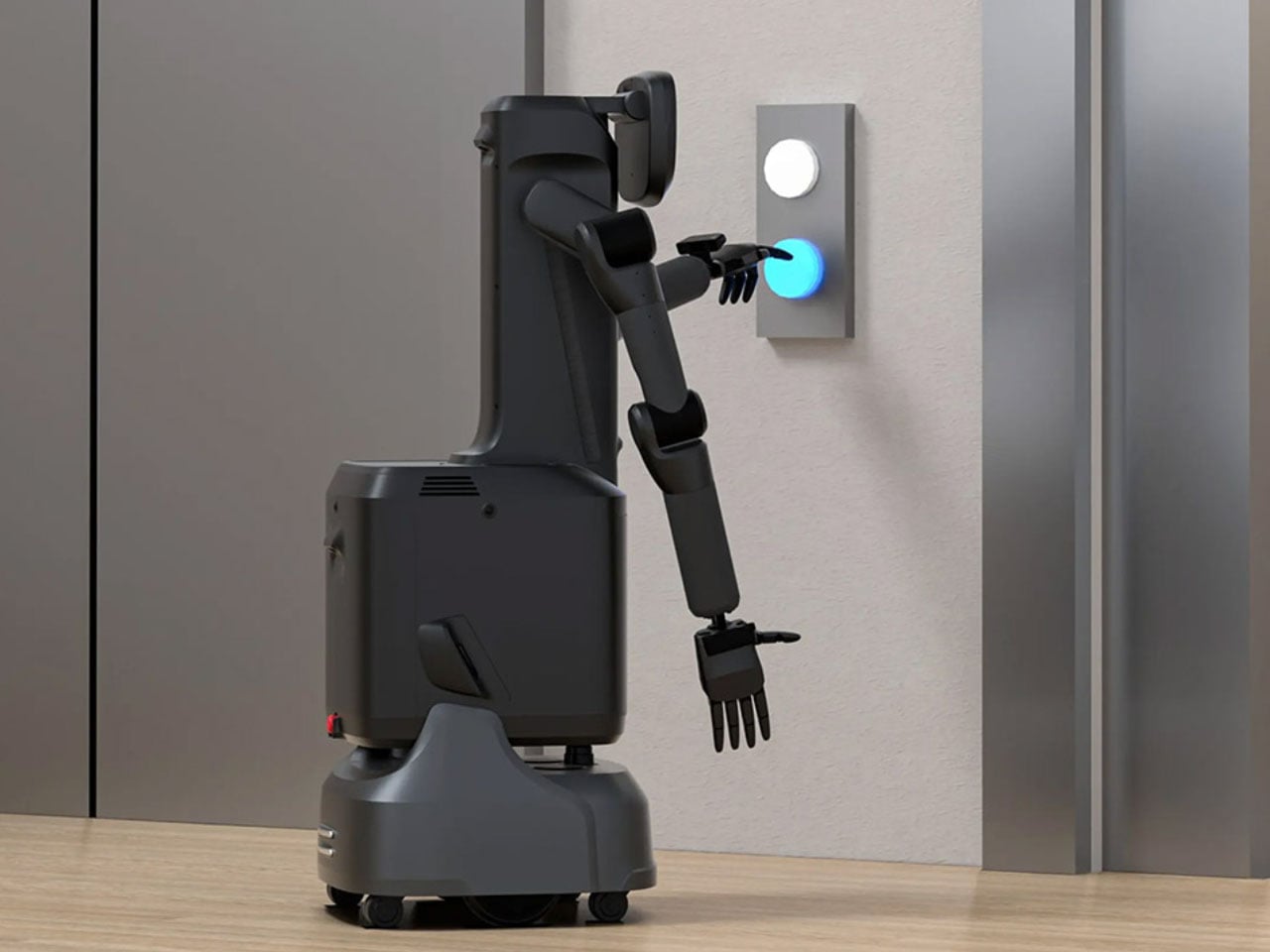
The growing global need for elder care and personal assistance is a challenge that demands innovative, heartfelt solutions. Imagine a robotic assistant in a nursing home—it’s not there to replace human interaction, but to supplement it, offering constant, tireless support. Its human-like form allows it to interact with tools and spaces designed for people, like opening a standard door or operating an elevator, making its help immediately practical.
This familiar, non-threatening design can foster a feeling of comfort and ease of use for the elderly and those with special needs. By handling repetitive or physically strenuous tasks, such as fetching items, monitoring vital signs, or providing simple, encouraging reminders, these humanoids free up human caregivers to focus on the essential, emotional elements of care. It’s about optimizing human effort, ensuring that every person receives the dignified attention they deserve.
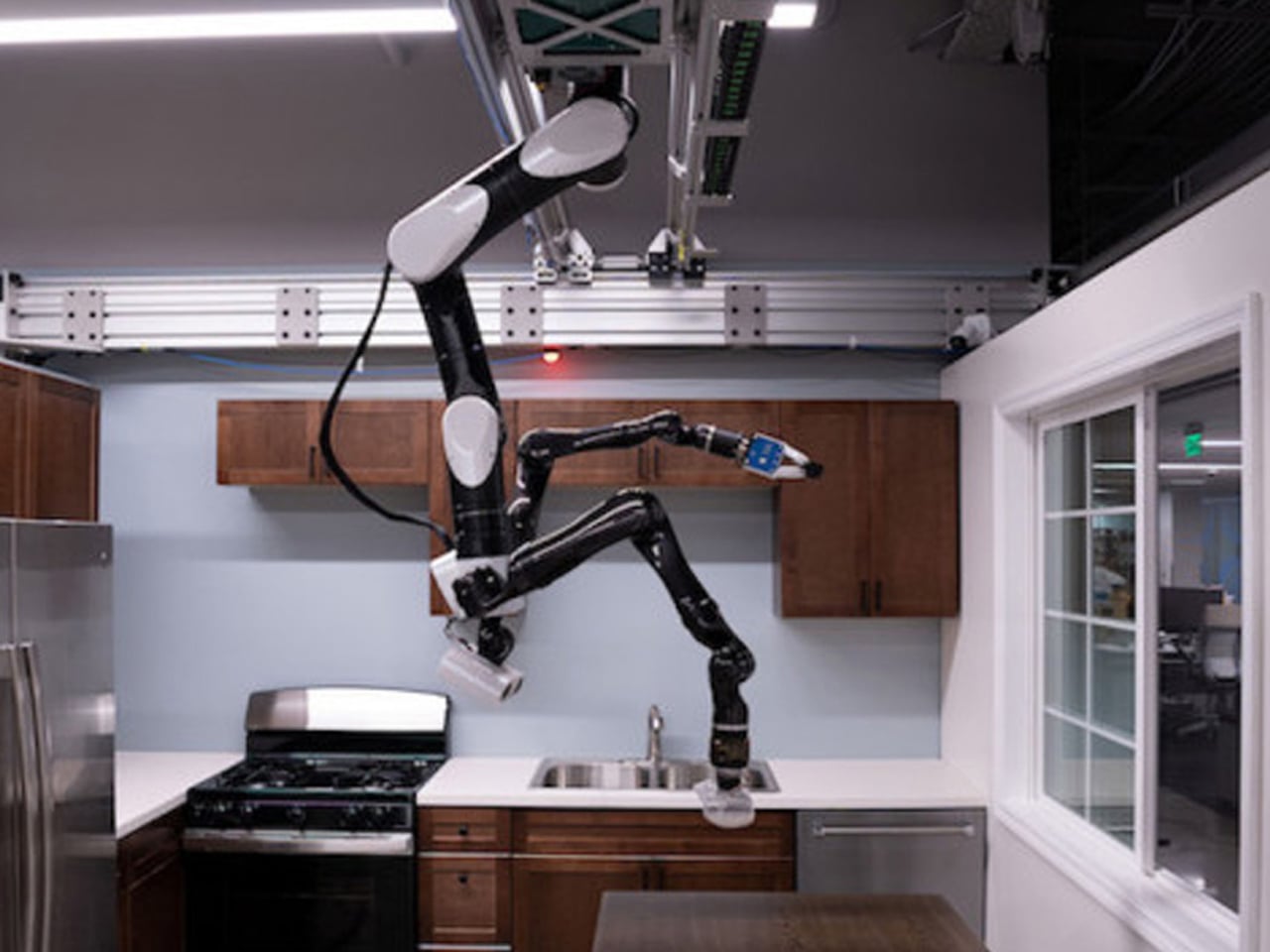
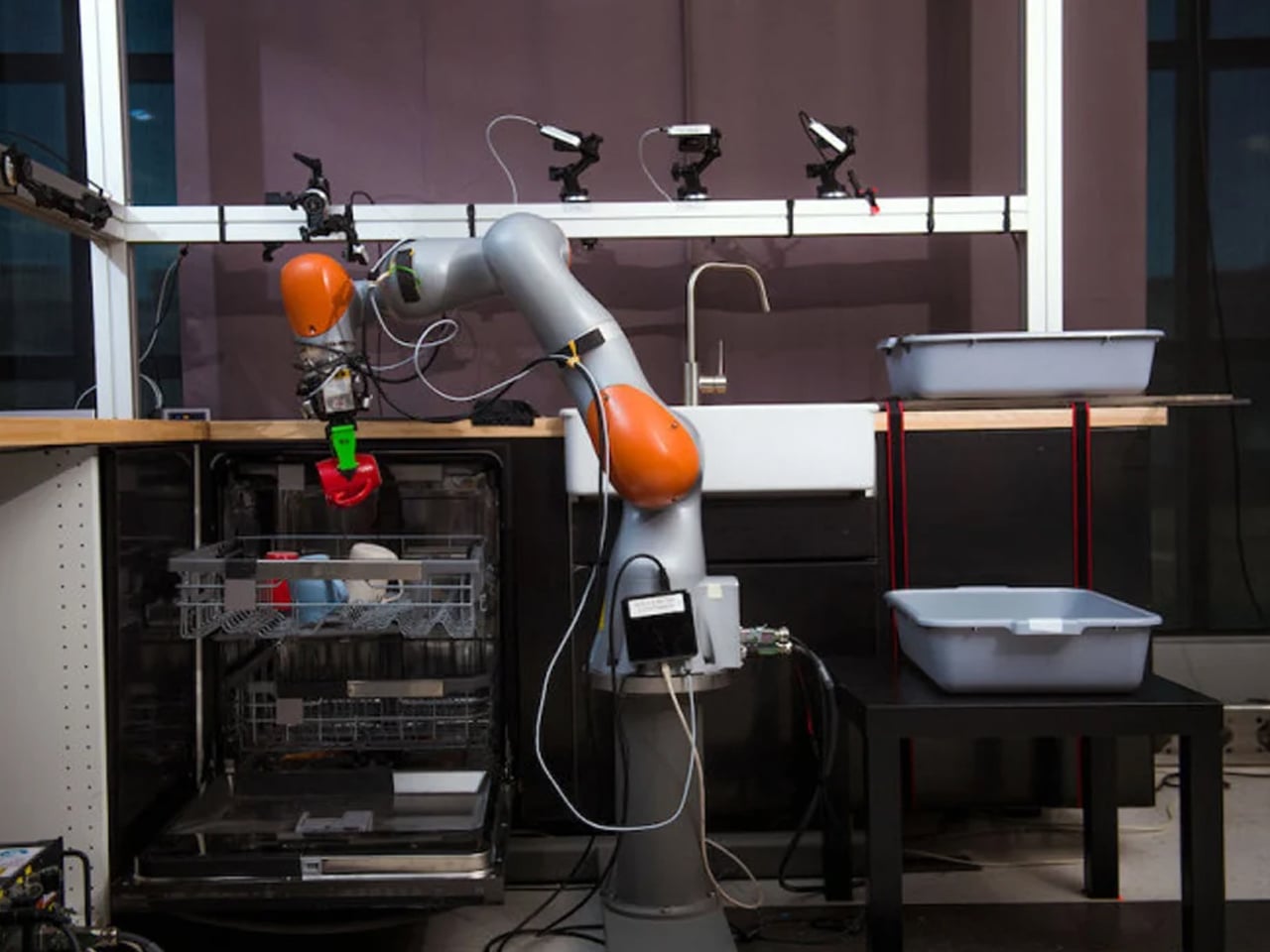


Toyota’s Gantry robot is designed to assist the elderly by performing household chores, offering a solution for the rapidly growing population over 65, who often lack tailored technological support. Unlike industrial robots operating in controlled factory environments, the home presents unstructured and diverse challenges. Developed by the Toyota Research Institute (TRI), the gantry robot is being tested in mock-up home settings in California and can handle tasks such as cleaning and loading the dishwasher. Inspired by Japanese home layouts, the robot is ceiling-mounted to overcome floor-space constraints, allowing it to operate efficiently while remaining unobtrusive.
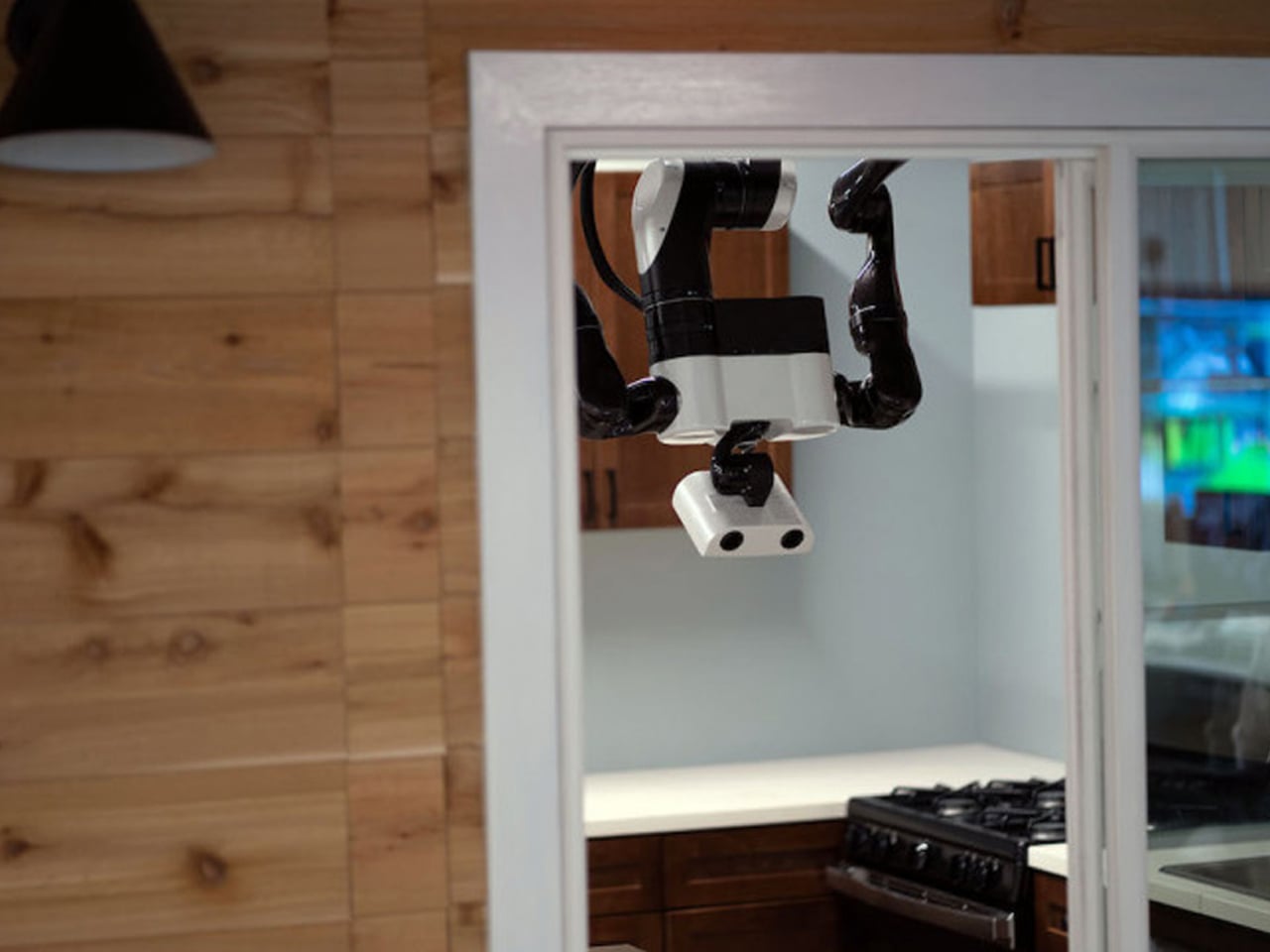


The gantry robot is part of a broader initiative at TRI to create a fleet of household-assistive robots, including floor-based mobile units and “soft bubble gripper” robots capable of gently handling objects. Using virtual reality, researchers train these robots by recording human actions, programming movements into the machines. While still in prototype stages, this innovative approach could redefine elder care and independent living by integrating robots into home architecture.
2. Simplifying Practical Household Help
Daily chores and specialized tasks can quickly consume your time, but human-like robots are designed to fit naturally into our homes. With two hands and two legs, they can use standard tools and appliances like vacuums, counters, or dishwashers without requiring costly modifications. Their familiar form makes them instantly practical and easy to integrate into everyday life.
Beyond basic chores, these robots can learn and perform complex sequences, turning your routine tasks into streamlined operations. By handling repetitive or time-consuming work, they free you to focus on what truly matters, enhancing convenience, efficiency, and well-being.
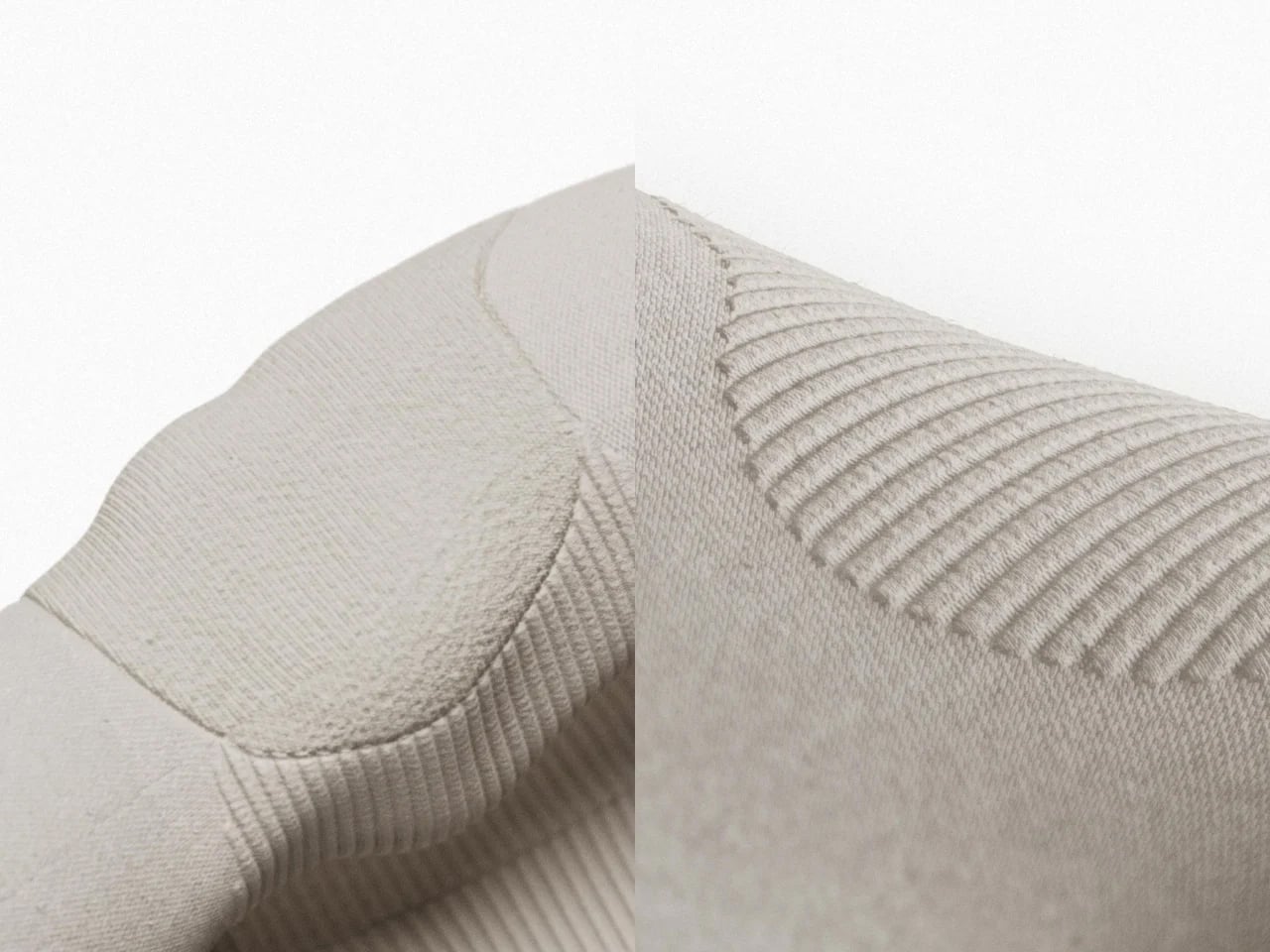


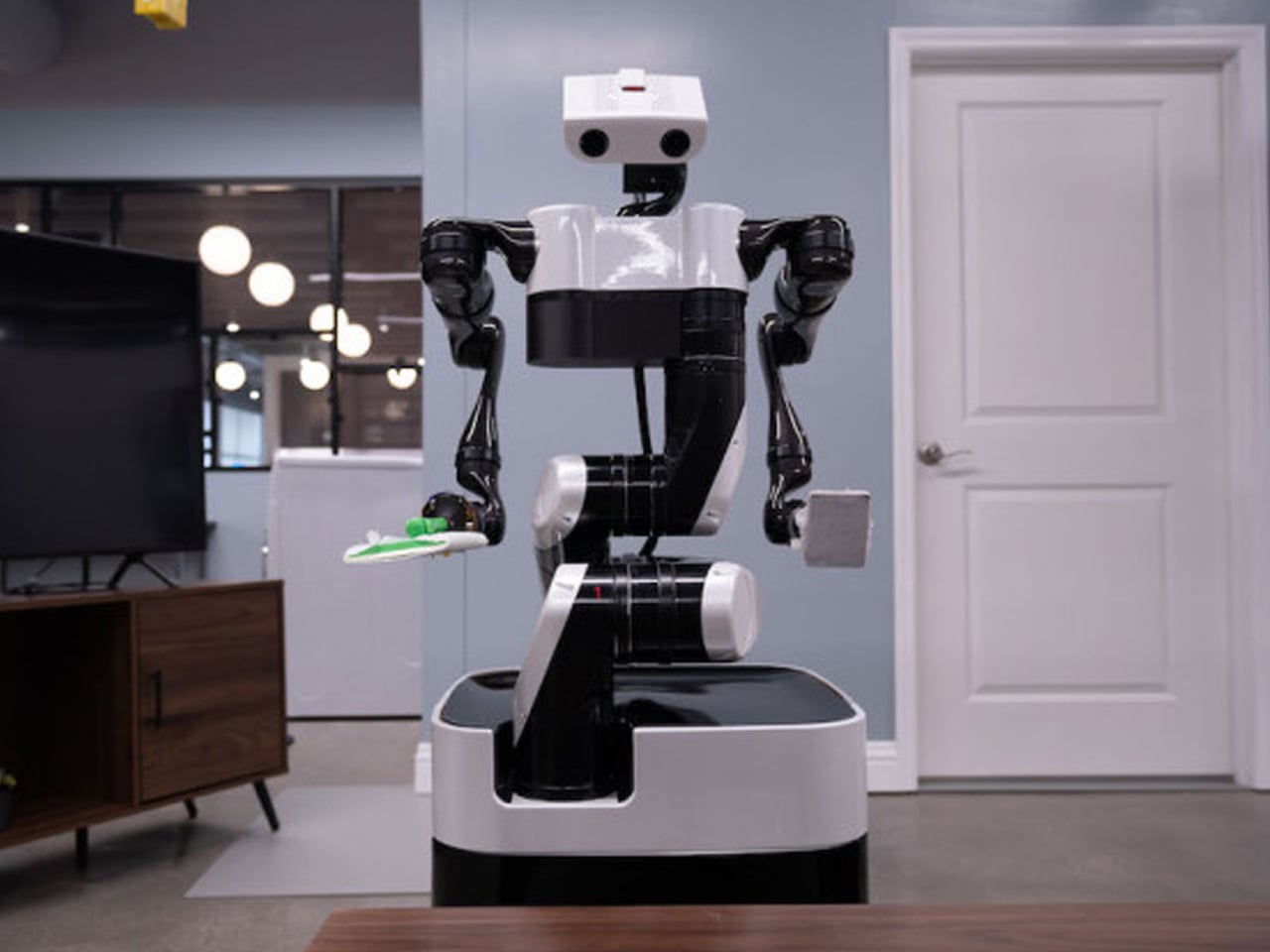
Humanoid robots have long fascinated us, yet their adoption in homes has been limited by overly mechanical designs. Traditional robots with rigid shells, exposed joints, and industrial aesthetics feel out of place among domestic furnishings. As the demand for robotic assistants, particularly for elderly care, rises, machines must be approachable and seamlessly integrate into human environments rather than appear intimidating.
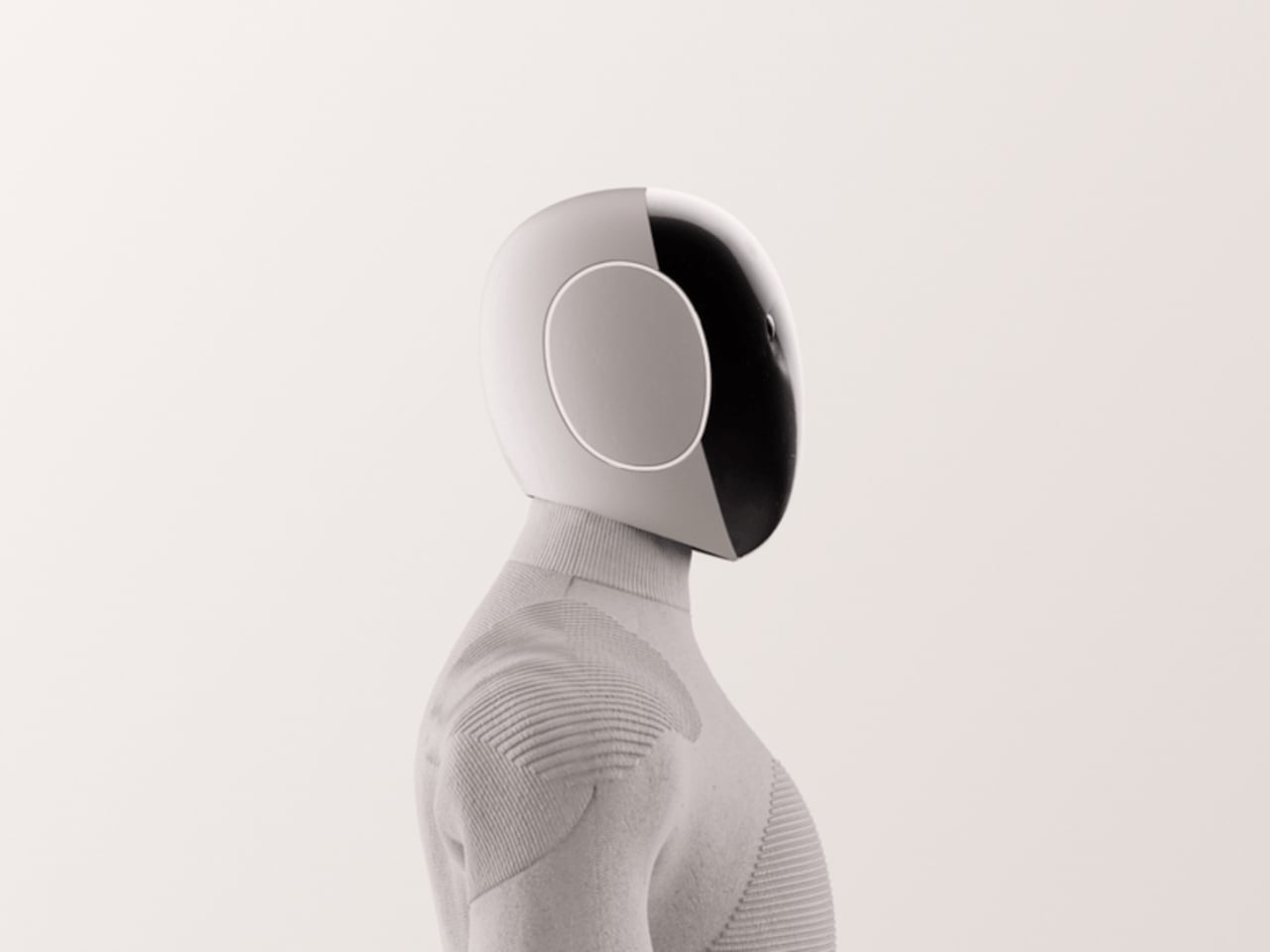


The NEO Gamma from 1X Technology exemplifies this shift. Its 3D-printed nylon fabric “skin” conceals machinery while allowing full mobility and quiet operation. Tendon-driven hands provide precise, gentle manipulation of household objects, and minimalist design elements, including custom shoes and illuminated ear rings, combine stability, intuitive communication, and visual appeal. NEO performs practical domestic tasks such as tidying, deep cleaning, and organizing, freeing household members to focus on meaningful activities. By blending functionality, dexterity, and approachable aesthetics, NEO demonstrates how humanoid robots can harmoniously coexist with humans and transform domestic assistance from novelty to necessity.
3. Enhancing Hotel Service with Robots
Many hotel tasks are repetitive, physically demanding, or time-consuming—like delivering luggage, restocking minibars, or cleaning rooms. Human staff performing these tasks constantly can experience fatigue, stress, and risk of injury. Service robots, designed with human-like form and capabilities, offer a reliable solution, performing these chores efficiently and safely.
By handling routine and labor-intensive duties, robots allow hotel employees to focus on personalized guest experiences, creative problem-solving, and management tasks. This integration boosts overall service quality, improves staff well-being, and ensures smoother, more efficient hotel operations, combining technology with hospitality for a smarter, safer environment.
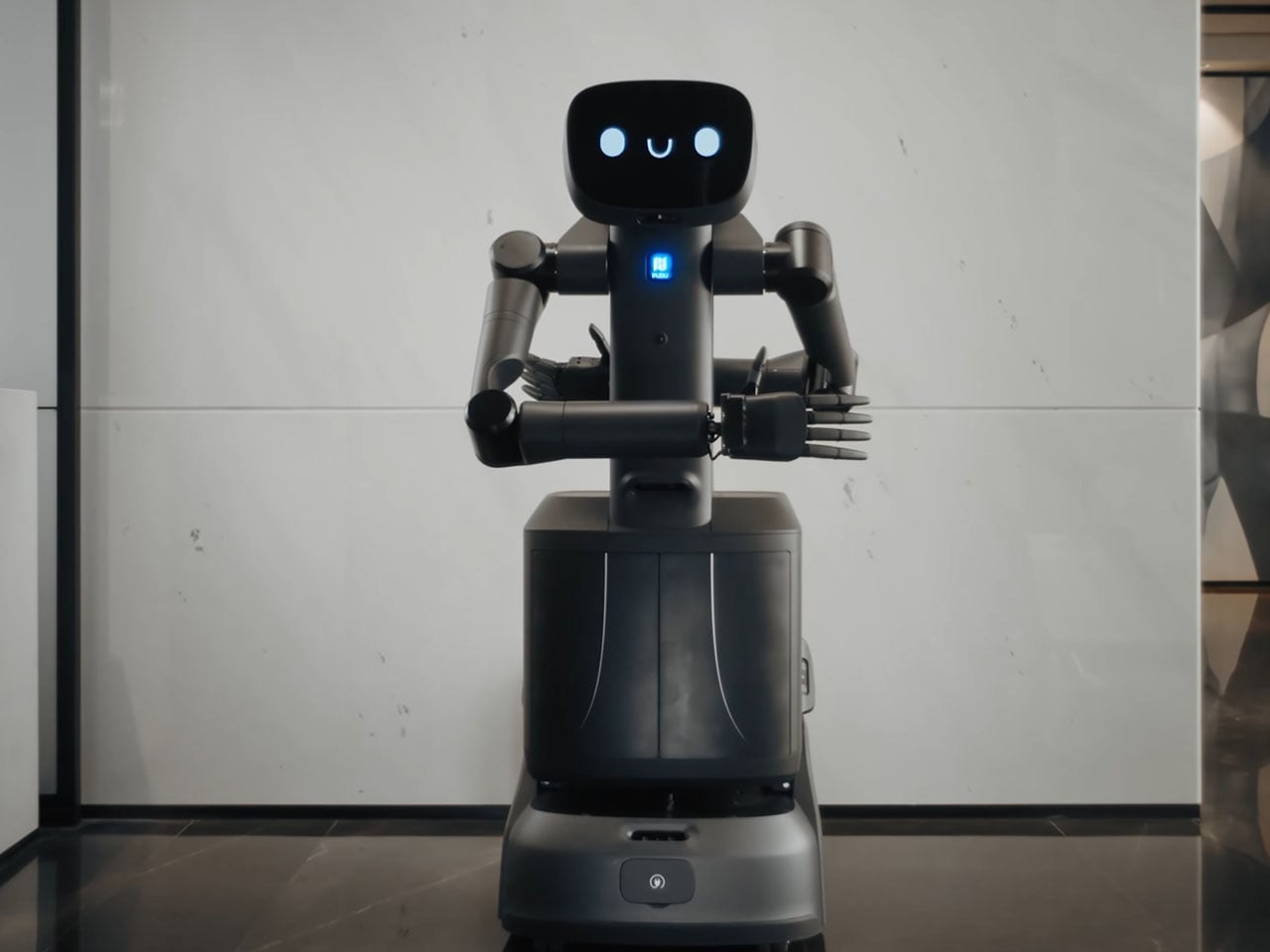


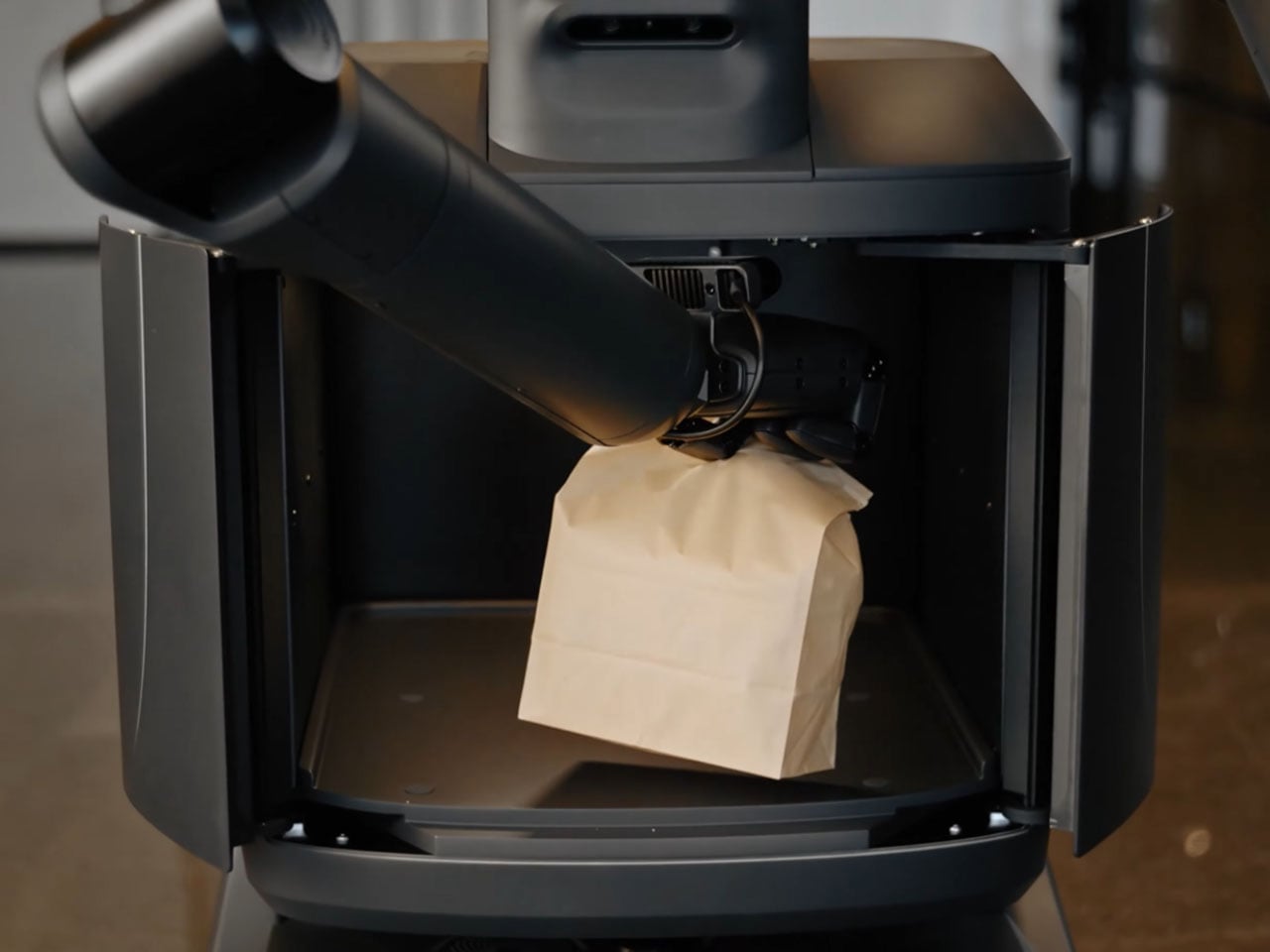
Chinese robotics companies are rapidly advancing the development of humanoid and AI-powered robots with practical commercial applications. Among the latest innovations, Pudu Robotics’ FlashBot Arm stands out as a semi-humanoid service robot designed for dynamic environments such as offices, hotels, restaurants, and healthcare facilities. Building on the company’s FlashBot Max wheeled model, the bipedal FlashBot Arm features dual 7-degree-of-freedom arms, PUDU DH11 hands with 11 degrees of freedom, a 10.1-inch touchscreen, and a spacious belly compartment for secure deliveries. These capabilities enable precise, human-like actions, including object handling, button operation, and interactive gestures, making it highly versatile for complex commercial tasks.
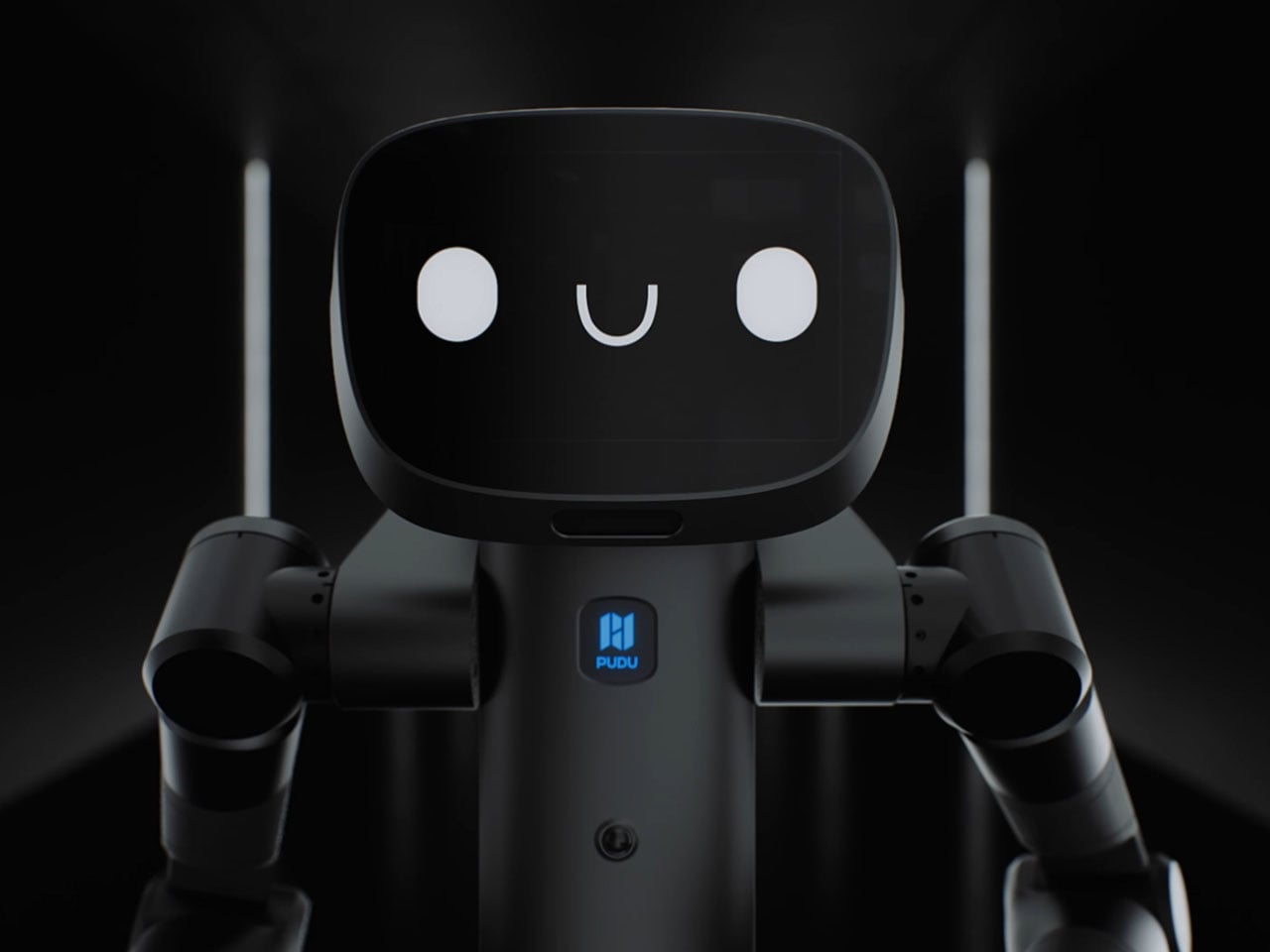


The robot integrates advanced AI and sensor technologies, including RGB depth cameras, panoramic lenses, LiDAR, and pressure-sensitive skin, managed through Pudu’s VSLAM system for real-time 3D mapping and obstacle navigation. Its AI-driven learning model allows autonomous adaptation to various tasks, while voice interaction and collaborative functionality enhance usability. Weighing 33 lb, the FlashBot Arm operates up to eight hours per charge and demonstrates a significant milestone in the commercialization of humanoid AI service robots.
4. Serving as Critical Tools in Hazardous Environments
In fields where human presence is risky or impossible, such as disaster zones or war-struck regions, humanoid robots provide vital operational support. These robots can navigate unstable terrain, assess structural damage, and perform rescue tasks, allowing rapid response without endangering human lives. By executing programmed maneuvers and adapting to real-time conditions, they turn complex strategies into actionable results, making them indispensable in search-and-rescue missions and emergency operations.
Beyond operational efficiency, these robots serve as dynamic tools for training and preparedness. Rescue personnel can simulate high-risk scenarios, program robot responses, and study outcomes, enhancing tactical learning and readiness. Their consistent performance and ability to operate under extreme conditions offer invaluable support, expanding the scope of humanitarian and emergency response while reducing exposure to danger for human teams.
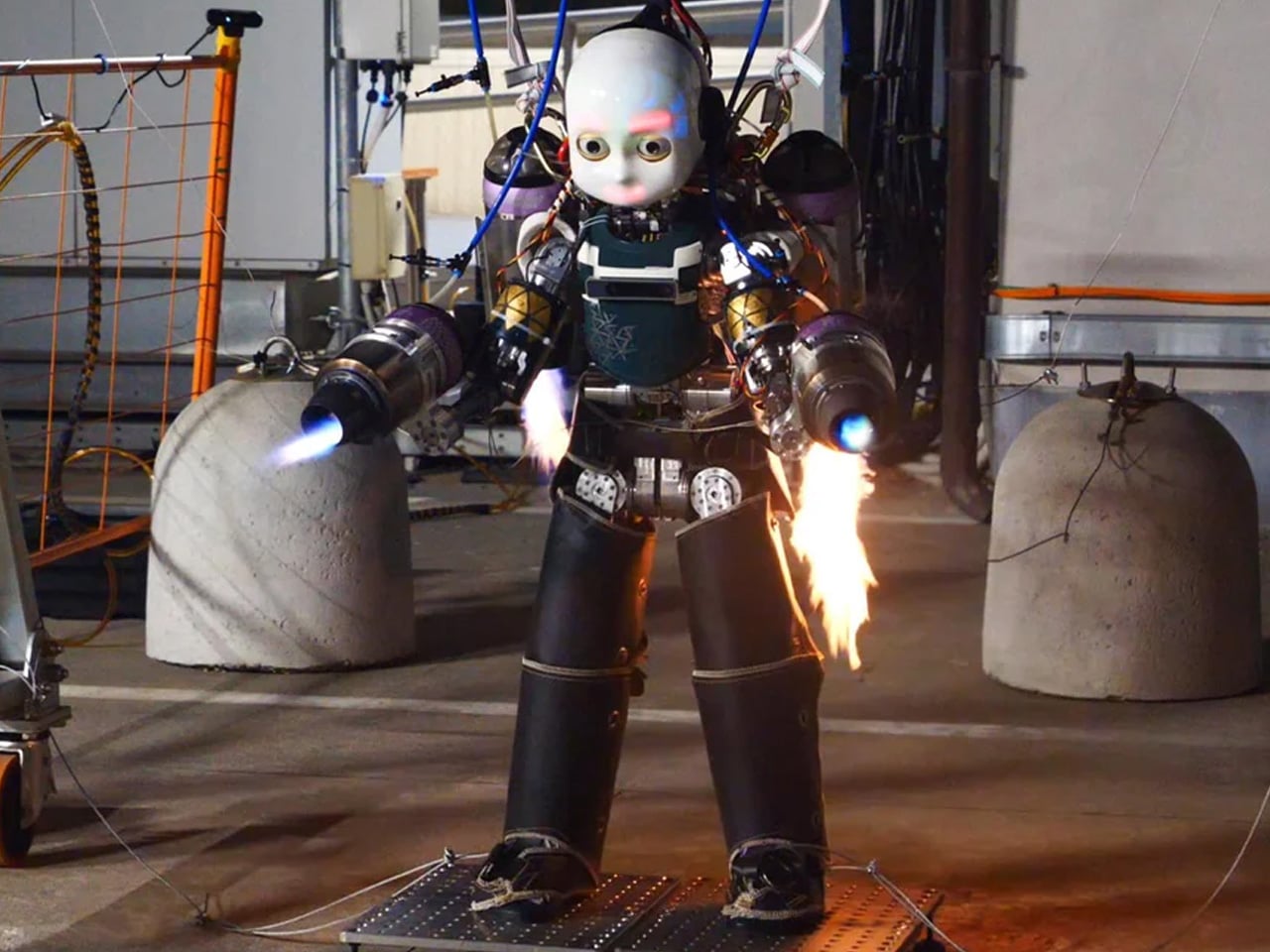

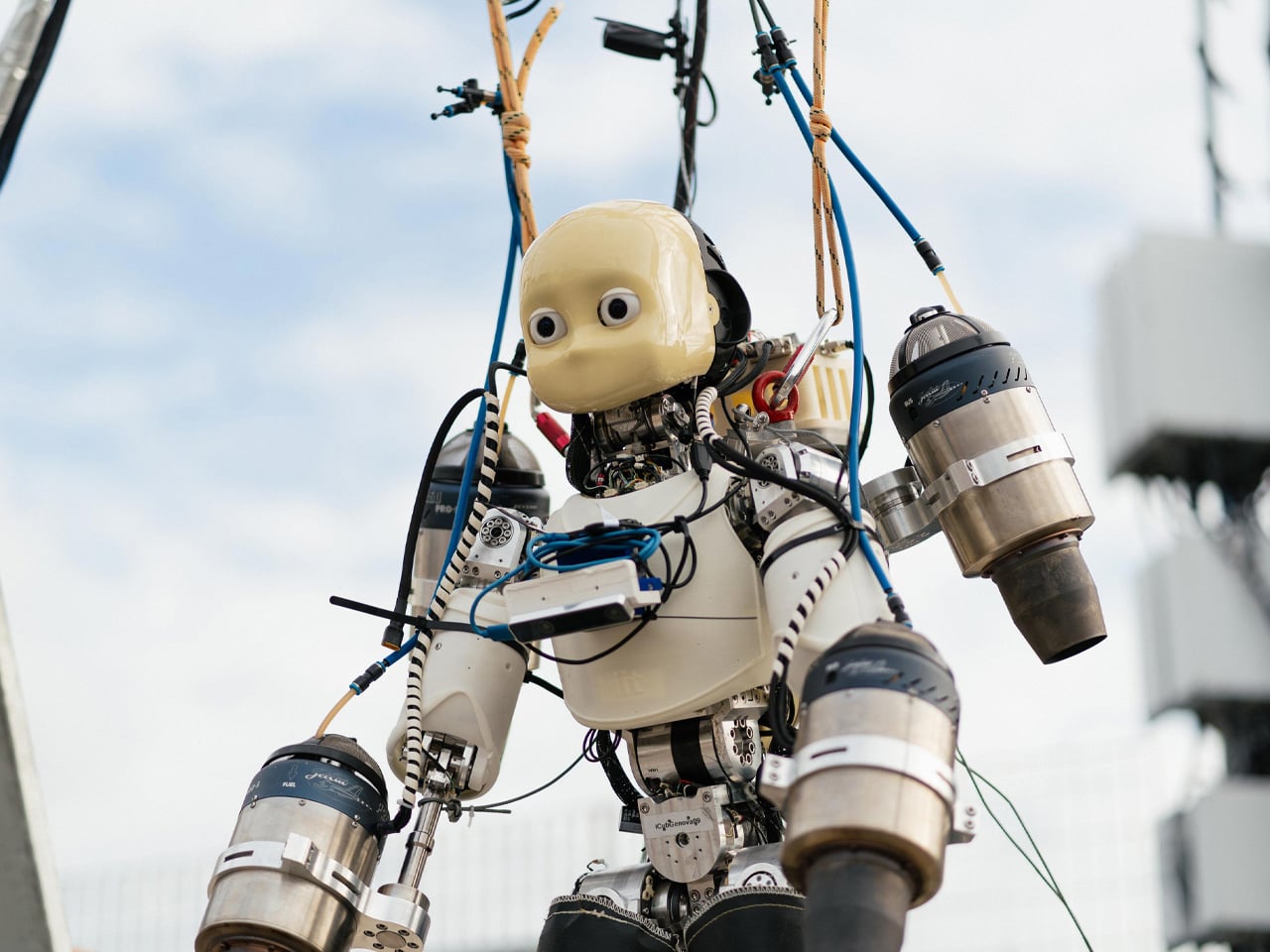
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) often operate in conflict zones such as Ukraine-Russia and Israel-Iran, typically for destructive purposes. In contrast, the jet-powered humanoid robot iRonCub3, developed by the Italian Institute of Technology (IIT), is designed for constructive applications, including search-and-rescue operations in disaster-struck or hazardous environments. Combining terrestrial mobility with aerial capabilities, iRonCub3 represents a major advancement in multimodal robotics. In its maiden flight, conducted in a controlled test area, the robot lifted 50 cm off the ground and remained stable, demonstrating the results of two years of research and multiple prototype tests.
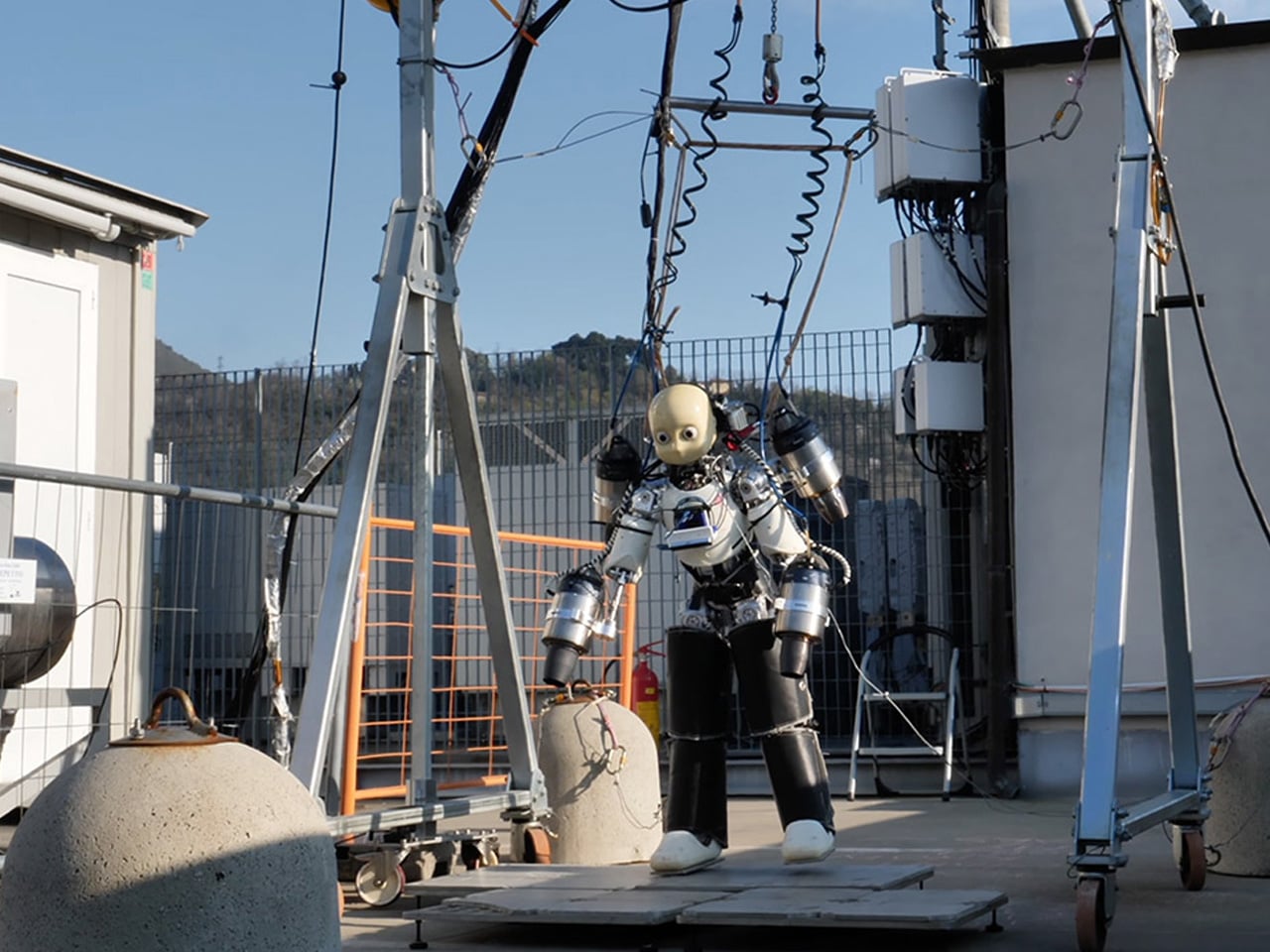

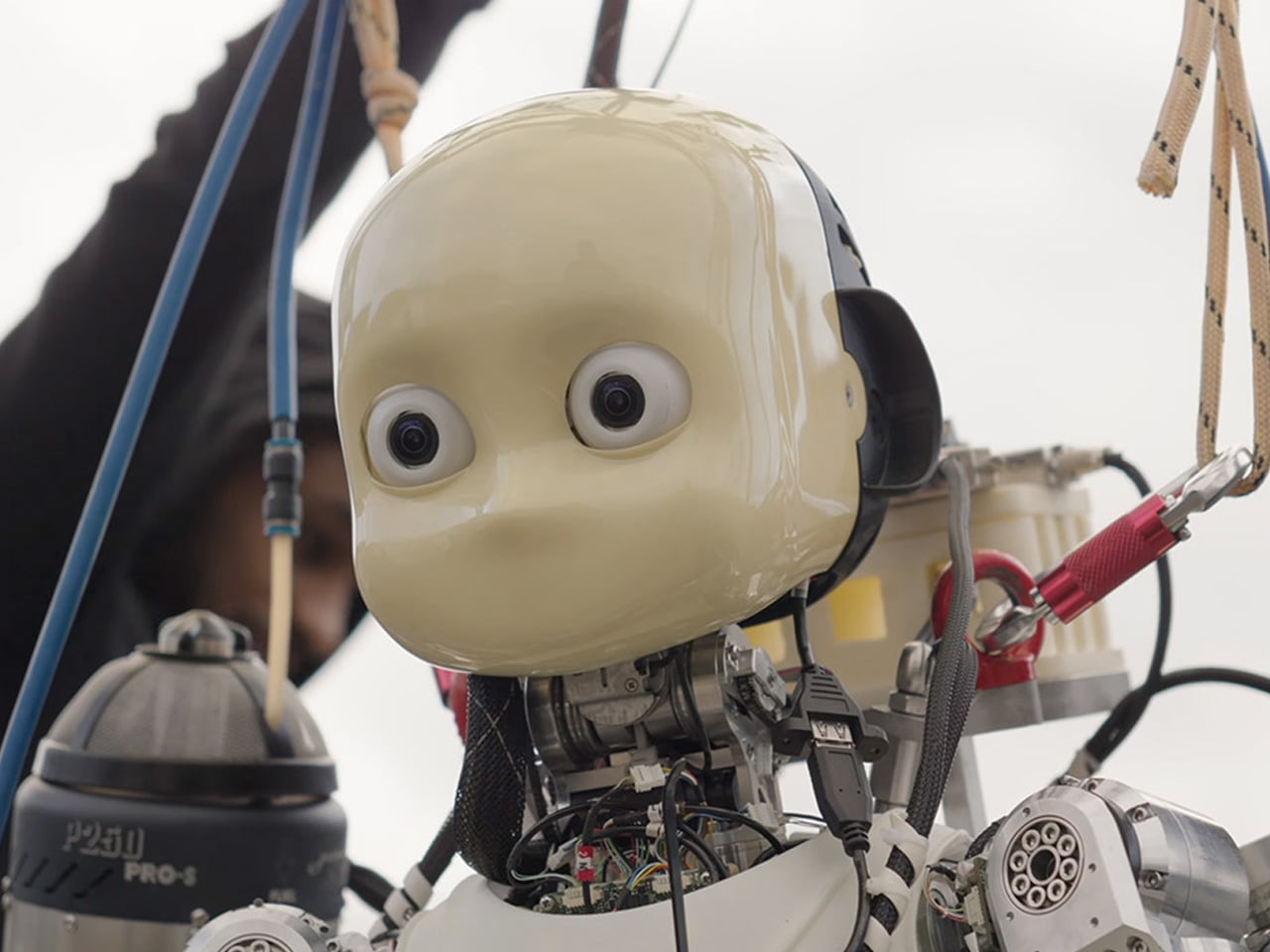
Weighing around 70 kg with four jet engines—two on its arms and two on a back-mounted jetpack—the iRonCub3 can generate over 1,000 newtons of thrust and withstand exhaust temperatures of 800°C, due to its titanium spine and heat-resistant protective covers. AI-driven control systems and optimally positioned turbines allow stable flight in uncertain conditions. Future testing at open sites aims to expand its operational potential, with applications in disaster response, hazardous environment navigation, and other autonomous robotic platforms.
5. Driving Breakthroughs in Human Movement and Design
Designing robots that move, balance, and interact like humans pushes engineers to study human physiology and biomechanics in unprecedented detail. This focus on biomimicry, learning from nature, is yielding breakthroughs that benefit people directly. For instance, improvements in robotic gait are informing better prosthetic limbs and exoskeletons, enhancing mobility for those with physical challenges.
Building human-like machines uncovers the subtle efficiency of our bodies and drives advances in materials, actuation, and control systems. By striving for versatile, stable, and strong robots, we gain insights that improve human performance, safety, and rehabilitation, turning robotic innovation into practical, life-changing solutions.
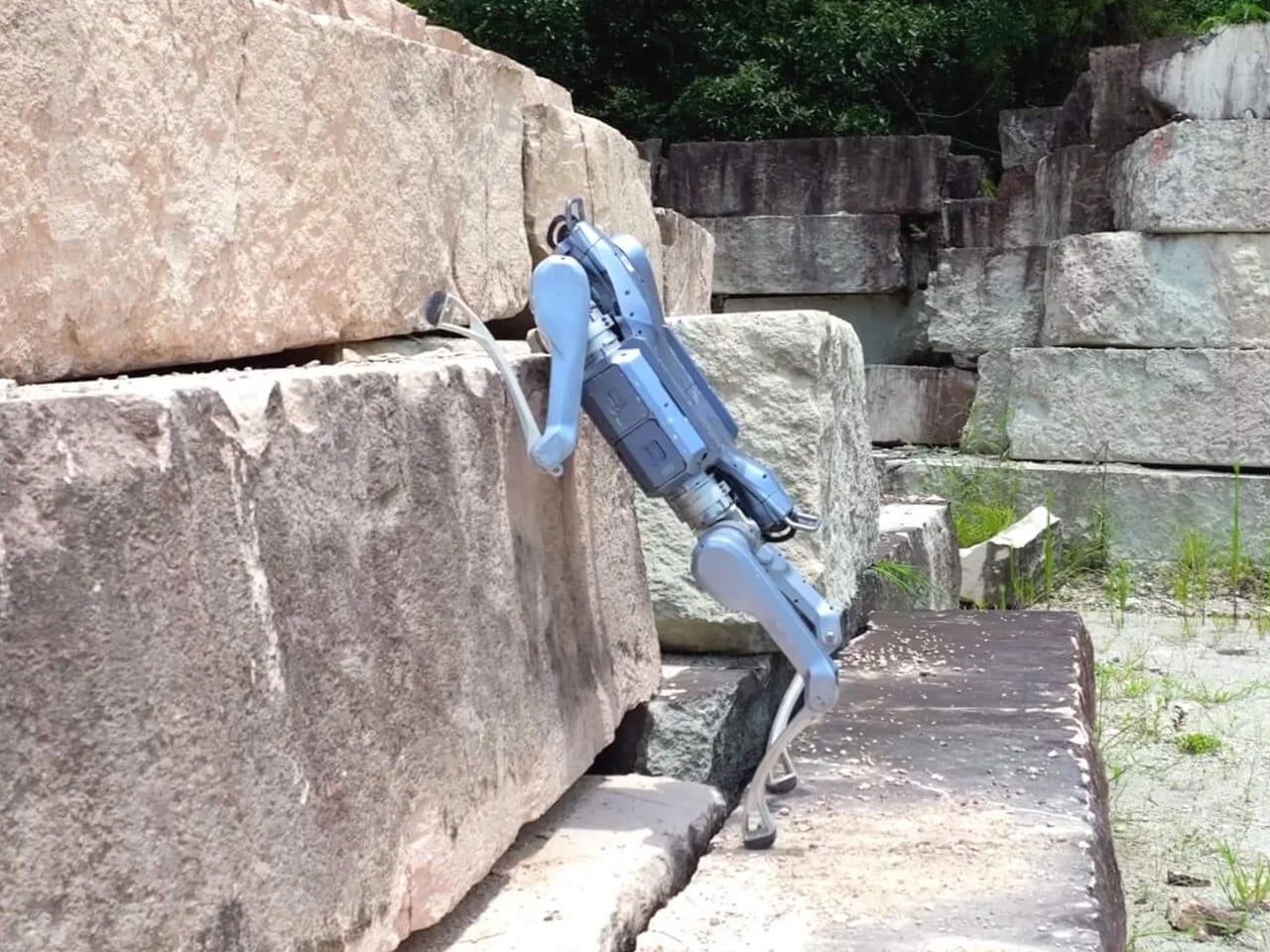
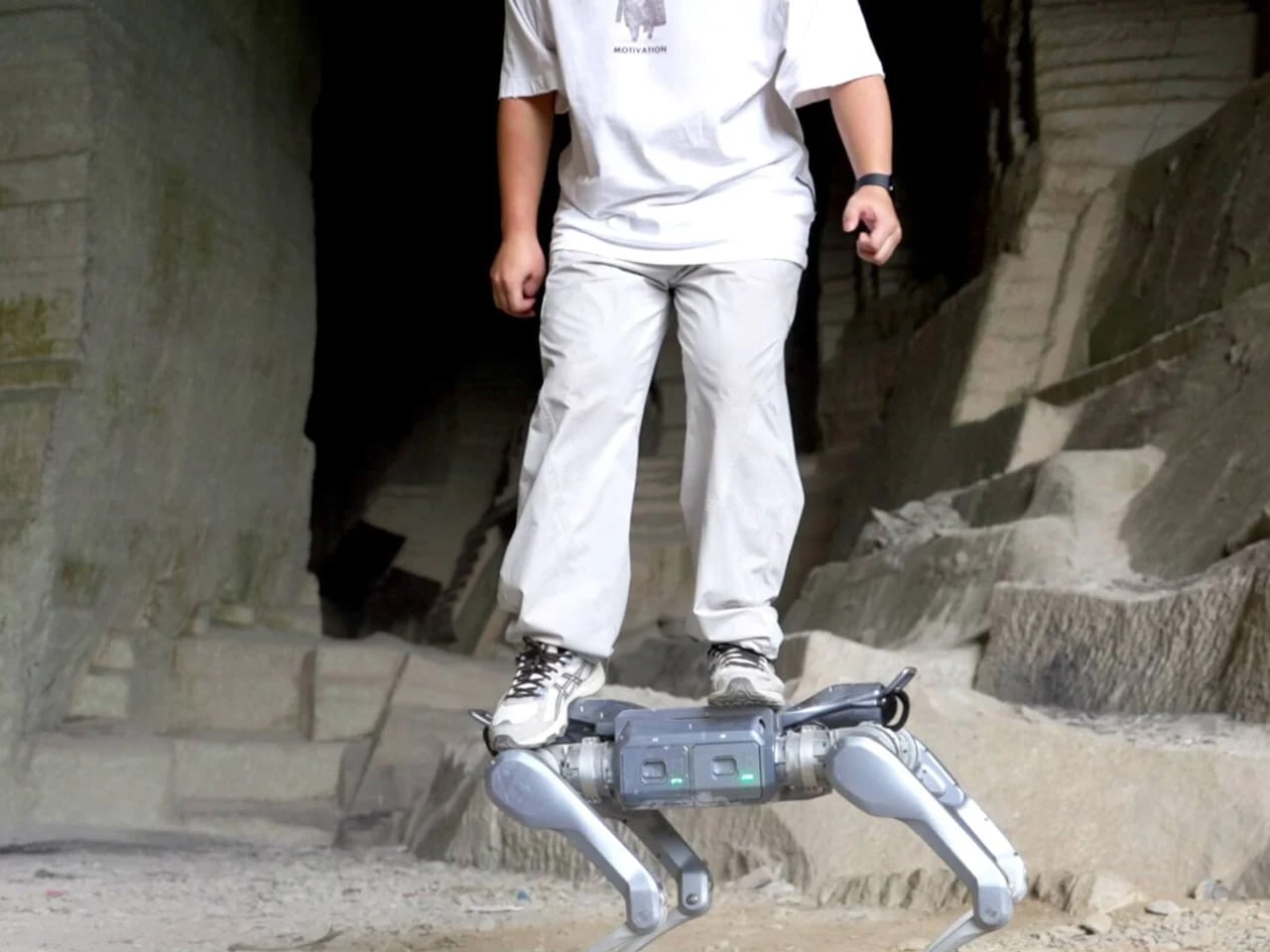


Unitree’s A2 Stellar Explorer marks a decisive advance in the evolution of quadruped robotics, moving the category beyond laboratory experimentation to rugged, real-world deployment. Engineered for harsh environments, the robot dog weighs 81 lbs, carries up to 55 lbs on inclines, sustains 220 lbs when stationary, and performs agile manoeuvres such as flips and jumps. It delivers up to 12 km of load-bearing travel per charge, operates for five hours unloaded, and reaches a top speed of 11.2 mph. With 180 Nm torque, a hot-swappable 9,000 mAh battery, dual LiDAR, AI vision, and an Intel Core i7, it navigates obstacles, steep gradients, and complex terrain autonomously. Connectivity is ensured via Wi-Fi 6, Bluetooth 5.2, and optional 4G/GPS.
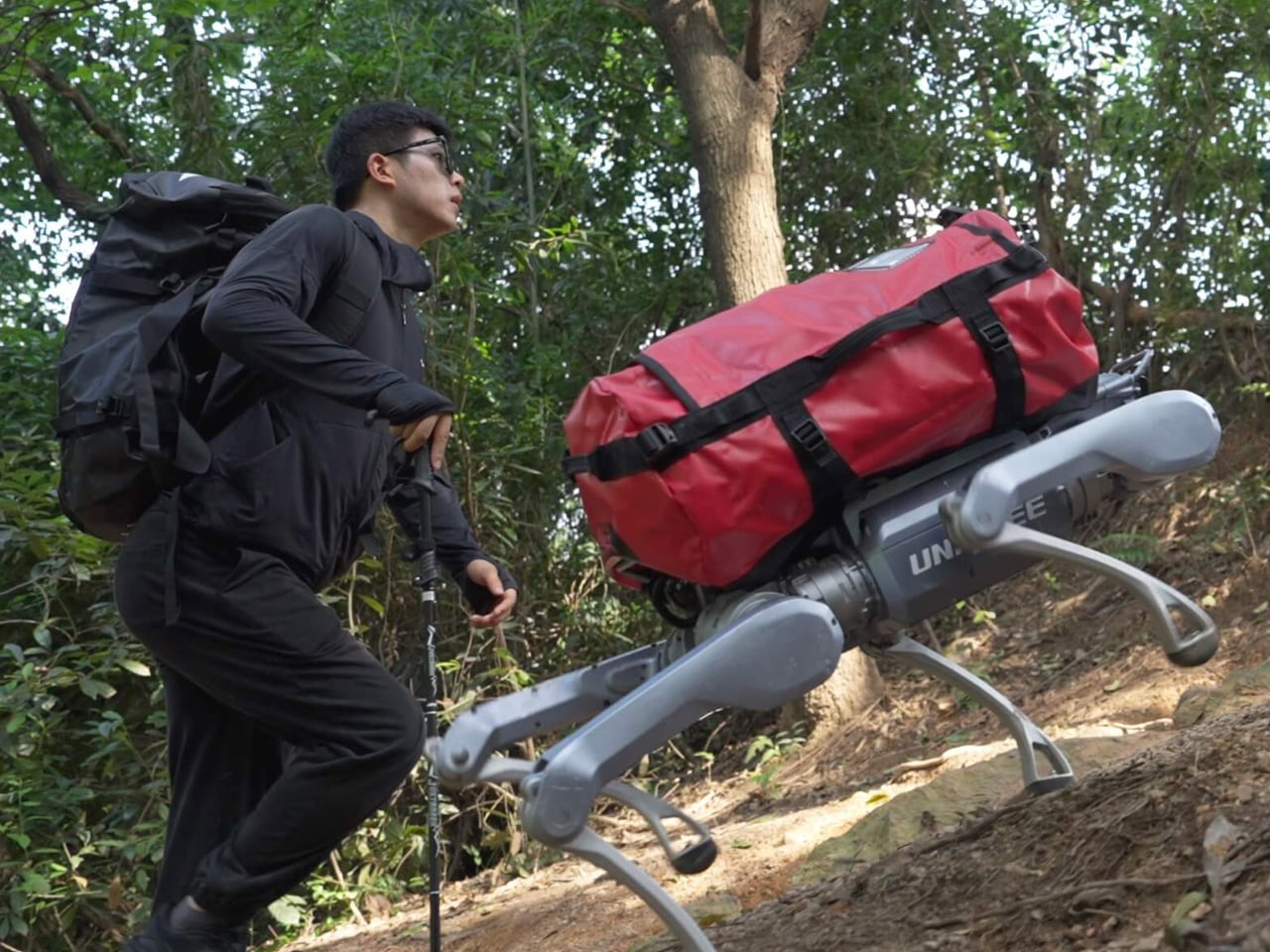
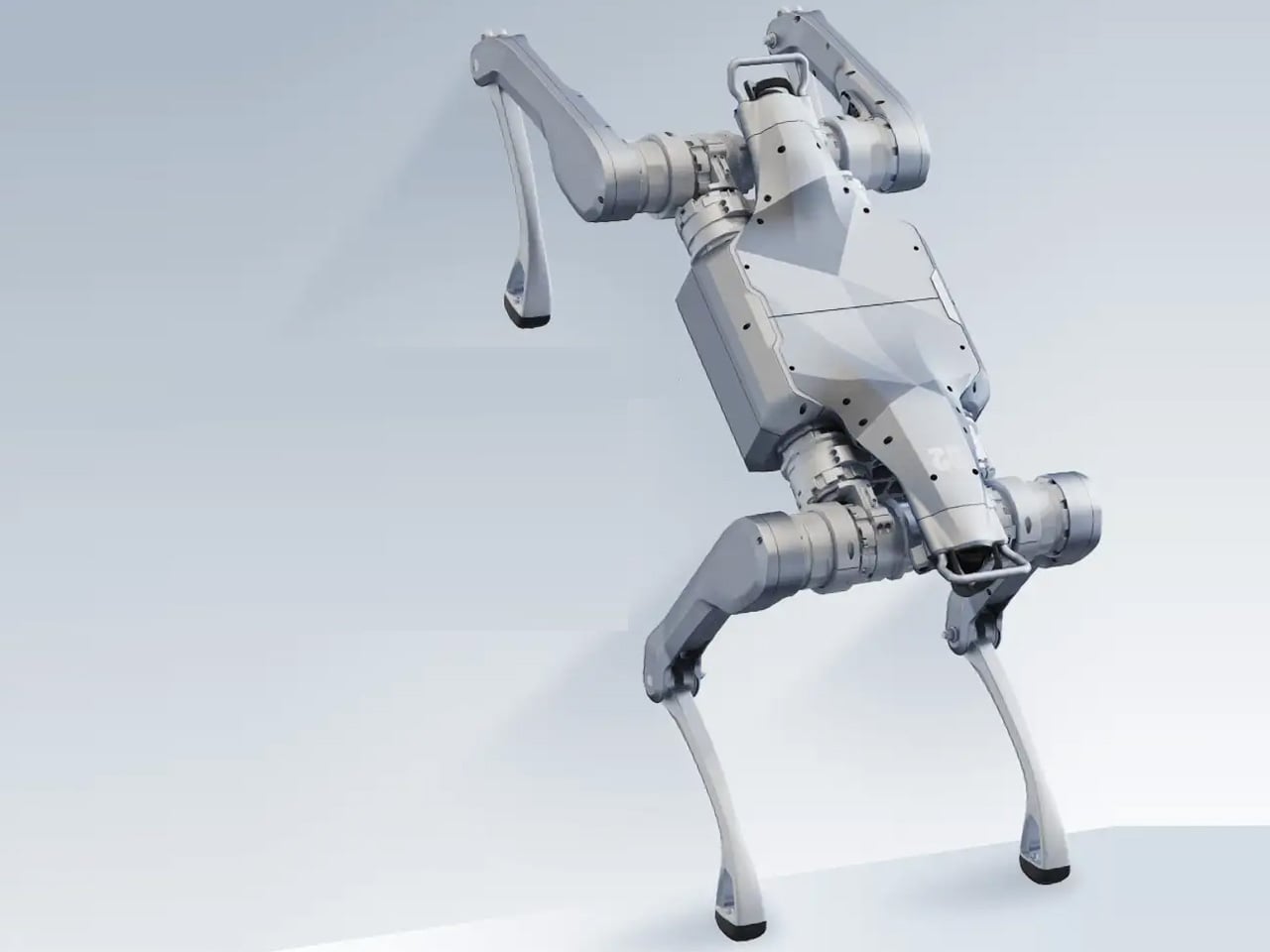


More than a technical showcase, the A2 signals a shift toward field-ready autonomous machines. Its payload capacity, endurance, and perception systems position it for applications in inspection, logistics, disaster response, and environmental monitoring where human presence is risky or impractical.
The future with human-like robots isn’t about replacing us, but it is about enhancing life. Like thoughtful interior design brings harmony to a home, these machines offer care support, demanding work, and education. By focusing on practical, helpful applications, we create a safer, more efficient, and well-supported world. This evolution combines technology with purpose, improving daily life for everyone.






